Benzene: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
imported>Nathaniel Gunby mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Chemistry - Benzene - Kekule Structure.png|right|350px|The commonly recognized, but somewhat inaccurate Kekulé representation of Benzene, which Kekulé said came to him in a dream}} | |||
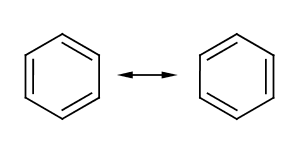
'''Benzene''' (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>) is a six carbon aromatic compound commonly used in industry as a precursor for other important aromatics such as toluene, or benzoic acid. The structure of benzene could not easily be determined due to its unusual electronic characteristics. | '''Benzene''' (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>) is a six carbon aromatic compound commonly used in industry as a precursor for other important aromatics such as toluene, or benzoic acid. The structure of benzene could not easily be determined due to its unusual electronic characteristics. While it appears to consist of alternating single and double bonds, it is more accurate to view it as being composed of 6 single bonds with the six electrons from the double bond in a ring. However, structures based on this fact tend to be less informative, so Kekule's representation is still used. | ||
Revision as of 17:25, 31 October 2010
Benzene (C6H6) is a six carbon aromatic compound commonly used in industry as a precursor for other important aromatics such as toluene, or benzoic acid. The structure of benzene could not easily be determined due to its unusual electronic characteristics. While it appears to consist of alternating single and double bonds, it is more accurate to view it as being composed of 6 single bonds with the six electrons from the double bond in a ring. However, structures based on this fact tend to be less informative, so Kekule's representation is still used.