Warfarin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk m (typo) |
imported>David E. Volk m (IUPAC name) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
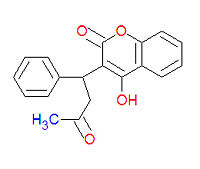
[[Image:Warfarin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Warfarin structure.jpg/credit|{{Warfarin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Structure of Warfarin.]] | [[Image:Warfarin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Warfarin structure.jpg/credit|{{Warfarin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Structure of Warfarin.]] | ||
'''Warfarin''' is a an [[anticoagulant]] medication used prophylactically to suppress the formation of [[thrombosis]] and [[embolism]]. It was originally designed to be a rat poison. It works as an anticogulant by suppressing the enzyme [[epoxide reductase]] in the liver, thereby suppresing the formation of the reduced form of [[vitamine K]] epoxide, which is needed for the synthesis of many coagulation factors. | '''Warfarin''' (IUPAC name | ||
4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-chromen-2-one) is a an [[anticoagulant]] medication used prophylactically to suppress the formation of [[thrombosis]] and [[embolism]]. It was originally designed to be a rat poison. It works as an anticogulant by suppressing the enzyme [[epoxide reductase]] in the liver, thereby suppresing the formation of the reduced form of [[vitamine K]] epoxide, which is needed for the synthesis of many coagulation factors. | |||
Revision as of 11:20, 22 January 2008
Warfarin (IUPAC name 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-chromen-2-one) is a an anticoagulant medication used prophylactically to suppress the formation of thrombosis and embolism. It was originally designed to be a rat poison. It works as an anticogulant by suppressing the enzyme epoxide reductase in the liver, thereby suppresing the formation of the reduced form of vitamine K epoxide, which is needed for the synthesis of many coagulation factors.