Fosfomycin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (CZMed) |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Fosfomycin structure.jpg|right|150px|Fosfomycin, an antibiotic}} | |||
'''Fosfomycin''', also called '''phosphomycin''', '''phosphonomycin''' and '''fosfonomycin''', is a broad spectrum [[antibiotic]] chemical produced by ''Streptomyces fradiae''. It is used to treat uncomplicated [[urinary tract infection]]s (UTIs) in females for susceptible ''[[Escherichia coli]]'' and ''[[Enterococcus faecalis]]'' strains. It concentrates in the kidneys and bladder, and also reduces nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity associated with platinum-based anti-tumor drugs. The [[phosphoenolpyruvate]] analog irreversibly inhibits the enzyme [[enolpyruvate transferase]], thus preventing the synthesis of [[N-acetylmuramic acid]], a chemical necessary for building bacterial [[peptidogycan]] cell walls. It is sold under the brand names Monurol® and Veramina®. | '''Fosfomycin''', also called '''phosphomycin''', '''phosphonomycin''' and '''fosfonomycin''', is a broad spectrum [[antibiotic]] chemical produced by ''Streptomyces fradiae''. It is used to treat uncomplicated [[urinary tract infection]]s (UTIs) in females for susceptible ''[[Escherichia coli]]'' and ''[[Enterococcus faecalis]]'' strains. It concentrates in the kidneys and bladder, and also reduces nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity associated with platinum-based anti-tumor drugs. The [[phosphoenolpyruvate]] analog irreversibly inhibits the enzyme [[enolpyruvate transferase]], thus preventing the synthesis of [[N-acetylmuramic acid]], a chemical necessary for building bacterial [[peptidogycan]] cell walls. It is sold under the brand names Monurol® and Veramina®. | ||
Revision as of 07:03, 8 June 2009
Fosfomycin, also called phosphomycin, phosphonomycin and fosfonomycin, is a broad spectrum antibiotic chemical produced by Streptomyces fradiae. It is used to treat uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) in females for susceptible Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis strains. It concentrates in the kidneys and bladder, and also reduces nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity associated with platinum-based anti-tumor drugs. The phosphoenolpyruvate analog irreversibly inhibits the enzyme enolpyruvate transferase, thus preventing the synthesis of N-acetylmuramic acid, a chemical necessary for building bacterial peptidogycan cell walls. It is sold under the brand names Monurol® and Veramina®.
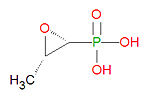
Its IUPAC chemical name is [(2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-yl]phosphonic acid and its chemical formula is C3H7O4P.
External links
The most up-to-date information about Fosfomycin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Fosfomycin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Fosfomycin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Fosfomycin - Detailed information from DrugBank.