Carbenicillin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (click HIDE MINOR EDITS to not see all of these!) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
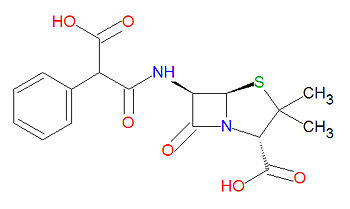
{{Image|Carbenicillin structure.jpg|right|350px|Carbenicillin}} | |||
'''Carbenicillin''', or '''carboxybenzylpenicillin''', is a broad-spectrum beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] and is a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including [[E. coli]], [[Enterobacter]] species, [[Enterococci]], [[Morganella morganii]], [[Proteus mirabilis]], [[Proteus vulgaris]], [[Pseudomonas]] and [[ | '''Carbenicillin''', or '''carboxybenzylpenicillin''', is a broad-spectrum beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] and is a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including [[E. coli]], [[Enterobacter]] species, [[Enterococci]], [[Morganella morganii]], [[Proteus mirabilis]], [[Proteus vulgaris]], [[Pseudomonas]] and [[Providencia rettgeri]]. | ||
== Mechanism of action== | |||
Like other beta-[[lactam]] penicillin derivatives, carbenicillin interference with final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by acylating the penicillin-sensitive [[transpeptidase]] enzyme's C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands, and leads to [[autolysis]] of the bacterial cells by the [[autolysin]] enzymes. | |||
==Chemistry == | |||
Carbenicillin is a beta-[[lactam]]-based antibiotic, which acylates a transpetidase enyzme through a lactam ring-opening reaction. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(3-hydroxy-3-oxo-2-phenylpropanoyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>17</sub>H<sub>18</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>S (MW = 378.3996 g/mol). | |||
== External links == | |||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 24 July 2024
Carbenicillin, or carboxybenzylpenicillin, is a broad-spectrum beta-lactam-based antibiotic and is a derivative of penicillin. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including E. coli, Enterobacter species, Enterococci, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas and Providencia rettgeri.
Mechanism of action
Like other beta-lactam penicillin derivatives, carbenicillin interference with final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by acylating the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase enzyme's C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands, and leads to autolysis of the bacterial cells by the autolysin enzymes.
Chemistry
Carbenicillin is a beta-lactam-based antibiotic, which acylates a transpetidase enyzme through a lactam ring-opening reaction. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(3-hydroxy-3-oxo-2-phenylpropanoyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C17H18N2O6S (MW = 378.3996 g/mol).
External links
The most up-to-date information about Carbenicillin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Carbenicillin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Carbenicillin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Carbenicillin - Detailed information from DrugBank.