Kansai: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Image|Kansa-Japan-map.png|right|180px|Location of Kansai.}} | {{Image|Kansa-Japan-map.png|right|180px|Location of Kansai.}} | ||
The exact borders of Kansai and the difference, if any, from the term 'Kinki' is a matter of some controversy. Six prefectures are indisputably within Kansai: [[Hyogo prefecture|Hyogo]], [[Kyoto prefecture|Kyoto]], [[Nara prefecture|Nara]], [[Osaka prefecture|Osaka]], [[Shiga prefecture|Shiga]] and [[Wakayama prefecture|Wakayama]]. [[Mie prefecture]] is also generally identified as part of Kansai, as are sometimes [[Fukui prefecture|Fukui]] and [[Tokushima prefecture|Tokushima]].<ref>This article assumes that Kansai comprises seven prefectures, excluding Fukui (in the [[Chubu]] region) and Tokushima (on the island of [[Shikoku]]). Official Mie prefectural information, however, suggests that Mie is in ''both'' Kansai and Chubu. See ''Mie Prefecture'': '[http://www.pref.mie.jp/ENGLISH/overview/e_p03.pdf Mie's Location]'.</ref> | The exact borders of Kansai and the difference, if any, from the term 'Kinki' is a matter of some controversy. Six prefectures are indisputably within Kansai: [[Hyogo prefecture|Hyogo]], [[Kyoto prefecture|Kyoto]], [[Nara prefecture|Nara]], [[Osaka prefecture|Osaka]], [[Shiga prefecture|Shiga]] and [[Wakayama prefecture|Wakayama]]. [[Mie prefecture]] is also generally identified as part of Kansai, as are sometimes [[Fukui prefecture|Fukui]] and [[Tokushima prefecture|Tokushima]].<ref>This article assumes that Kansai comprises seven prefectures, excluding Fukui (in the [[Chubu]] region) and Tokushima (on the island of [[Shikoku]]). Official Mie prefectural information, however, suggests that Mie is in ''both'' Kansai and Chubu (more precisely, the [[Tokai]] sub-region of Chubu). See ''Mie Prefecture'': '[http://www.pref.mie.jp/ENGLISH/overview/e_p03.pdf Mie's Location]'.</ref> | ||
The total population of the Kansai region was 22,754,000 in 2006.<ref>''Japan Statistical Yearbook'': '[http://www.stat.go.jp/data/nenkan/zuhyou/y0203000.xls Population by Prefecture 1920-2006]'. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. .xls document.</ref> The area forms part of an urban corridor running north-eastwards towards [[Tokyo]] via the [[Chubu]] and [[Kanto]] regions; this makes Kansai part of one of the most densely-populated areas of the world, home to over half the country's population.<ref>''Japan Times'': '[http://search.japantimes.co.jp/mail/nn20070803a2.html Population shrinks again despite increase in births]'. 3rd August 2007.</ref> | The total population of the Kansai region was 22,754,000 in 2006.<ref>''Japan Statistical Yearbook'': '[http://www.stat.go.jp/data/nenkan/zuhyou/y0203000.xls Population by Prefecture 1920-2006]'. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. .xls document.</ref> The area forms part of an urban corridor running north-eastwards towards [[Tokyo]] via the [[Chubu]] and [[Kanto]] regions; this makes Kansai part of one of the most densely-populated areas of the world, home to over half the country's population.<ref>''Japan Times'': '[http://search.japantimes.co.jp/mail/nn20070803a2.html Population shrinks again despite increase in births]'. 3rd August 2007.</ref> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{main|Kyoto prefecture}} | {{main|Kyoto prefecture}} | ||
====Kyoto (京都市 ''Kyooto-shi'')==== | ====Kyoto (京都市 ''Kyooto-shi'')==== | ||
{{main|Kyoto}} | {{main|Kyoto (city)}} | ||
===Osaka prefecture (大阪府 ''Oosaka-fu'')=== | ===Osaka prefecture (大阪府 ''Oosaka-fu'')=== | ||
{{main|Osaka prefecture}} | {{main|Osaka prefecture}} | ||
====Osaka (大阪市 ''Oosaka-shi'')==== | ====Osaka (大阪市 ''Oosaka-shi'')==== | ||
{{main|Osaka}} | {{main|Osaka (city)}} | ||
Osaka is the capital of the prefecture, and a major centre of commerce. It is also known as a gastronomic centre - the 'Kitchen of Japan'<ref>''Osakacityguide.com'': '[http://www.osakacityguide.com/city-information/the-culinary-history-of-osaka.html The Culinary History of Osaka]'.</ref> (天下の台所 ''Tenka no Daidokoro'') - and for the distinctive local [[Japanese language|Japanese]] [[dialect]]. | Osaka is the capital of the prefecture, and a major centre of commerce. It is also known as a gastronomic centre - the 'Kitchen of Japan'<ref>''Osakacityguide.com'': '[http://www.osakacityguide.com/city-information/the-culinary-history-of-osaka.html The Culinary History of Osaka]'.</ref> (天下の台所 ''Tenka no Daidokoro'') - and for the distinctive local [[Japanese language|Japanese]] [[dialect]]. | ||
[[Image:Gozaisho-sign.jpg|right|thumb|250px| | [[Image:Gozaisho-sign.jpg|right|thumb|250px|A sign marks one spot where [[Shiga prefecture|Shiga]] and [[Mie prefecture|Mie]] prefectures meet, at the summit of Mount Gozaisho (御在所). The area is reached by cable car and ski lift from Yunoyama Onsen station (湯の山温泉駅) in Mie.]] | ||
===Mie prefecture (三重県 ''Mie-ken'')=== | ===Mie prefecture (三重県 ''Mie-ken'')=== | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
===Wakayama prefecture (和歌山県 ''Wakayama-ken'')=== | ===Wakayama prefecture (和歌山県 ''Wakayama-ken'')=== | ||
{{main|Wakayama prefecture}} | {{main|Wakayama prefecture}} | ||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
* | *Farnie, Douglas A. et al. ''Region and Strategy in Britain and Japan: Business in Lancashire and Kansai, 1890-1990.'' (2000). 322 pp. | ||
* | *Trewartha, Glenn T. ''Japan: A Geography'' (1965). | ||
==Footnotes== | ==Footnotes== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
*[[Chubu]] | *[[Chubu]] | ||
*[[Honshu]] | *[[Honshu]] | ||
*[[Japan]] | *[[Japan]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 7 September 2024
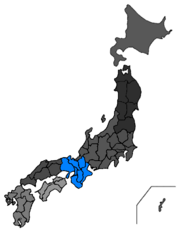
Kansai (関西地方 Kansai-chihoo), also known as Kinki (近畿地方 Kinki-chihoo), is a region of Japan located on Honshu island. It consists of seven administrative areas (prefectures), and is home to the cities of Kyoto and Osaka, among others.
The exact borders of Kansai and the difference, if any, from the term 'Kinki' is a matter of some controversy. Six prefectures are indisputably within Kansai: Hyogo, Kyoto, Nara, Osaka, Shiga and Wakayama. Mie prefecture is also generally identified as part of Kansai, as are sometimes Fukui and Tokushima.[1]
The total population of the Kansai region was 22,754,000 in 2006.[2] The area forms part of an urban corridor running north-eastwards towards Tokyo via the Chubu and Kanto regions; this makes Kansai part of one of the most densely-populated areas of the world, home to over half the country's population.[3]
Regions and cities
Kyoto prefecture (京都府 Kyooto-fu)
Kyoto (京都市 Kyooto-shi)
Osaka prefecture (大阪府 Oosaka-fu)
Osaka (大阪市 Oosaka-shi)
Osaka is the capital of the prefecture, and a major centre of commerce. It is also known as a gastronomic centre - the 'Kitchen of Japan'[4] (天下の台所 Tenka no Daidokoro) - and for the distinctive local Japanese dialect.
Mie prefecture (三重県 Mie-ken)
Mie's best-known site is the city of Ise (伊勢市 Ise-shi) and its Shinto (神道 Shintoo) shrines; these are collectively referred to as the 'Ise Shrine' (伊勢神宮 Ise-jinguu) and are considered the centre of Japan's native religion.
Shiga prefecture (滋賀県 Shiga-ken)
Nara prefecture (奈良県 Nara-ken)
Hyogo prefecture (兵庫県 Hyoogo-ken)
Wakayama prefecture (和歌山県 Wakayama-ken)
Bibliography
- Farnie, Douglas A. et al. Region and Strategy in Britain and Japan: Business in Lancashire and Kansai, 1890-1990. (2000). 322 pp.
- Trewartha, Glenn T. Japan: A Geography (1965).
Footnotes
- ↑ This article assumes that Kansai comprises seven prefectures, excluding Fukui (in the Chubu region) and Tokushima (on the island of Shikoku). Official Mie prefectural information, however, suggests that Mie is in both Kansai and Chubu (more precisely, the Tokai sub-region of Chubu). See Mie Prefecture: 'Mie's Location'.
- ↑ Japan Statistical Yearbook: 'Population by Prefecture 1920-2006'. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. .xls document.
- ↑ Japan Times: 'Population shrinks again despite increase in births'. 3rd August 2007.
- ↑ Osakacityguide.com: 'The Culinary History of Osaka'.