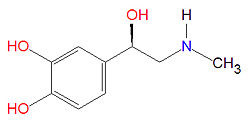
Epinephrine: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|casnumber= 51-43-4 | |casnumber= 51-43-4 | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Epinephrine''' (or ''' | '''Epinephrine''' (or '''adrenaline''') is a [[sympathomimetic]] and [[catecholamine]] that is a "active sympathomimetic [[hormone]] from the adrenal medulla in most species. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- [[sympathetic nervous system|adrenergic systems]], causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. It is used in [[asthma]] and cardiac failure and to delay absorption of local anesthetics."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | ||
==Administration== | ==Administration== | ||
As the dose of epinephrine is sometimes expressed as a ratio only (1 mL of 1:1000) or a concentration only (1 mg in 1 mL), [[medical error]]s in administration may be made. <ref name="pmid18166759">{{cite journal |author=Wheeler DW, Carter JJ, Murray LJ, ''et al'' |title=The effect of drug concentration expression on epinephrine dosing errors: a randomized trial |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=148 |issue=1 |pages=11–4 |year=2008 |month=January |pmid=18166759 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18166759 |issn=}}</ref> | As the dose of epinephrine is sometimes expressed as a ratio only (1 mL of 1:1000) or a concentration only (1 mg in 1 mL), [[medical error]]s in administration may be made. <ref name="pmid18166759">{{cite journal |author=Wheeler DW, Carter JJ, Murray LJ, ''et al'' |title=The effect of drug concentration expression on epinephrine dosing errors: a randomized trial |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=148 |issue=1 |pages=11–4 |year=2008 |month=January |pmid=18166759 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18166759 |issn=}}</ref> This problem is compounded by the availability of 1:1000 and 1:10,000 concentrations for, respectively, subcutaneous and intramuscular, versus intravenous, use. | ||
===Subcutaneous and intramuscular administration=== | ===Subcutaneous and intramuscular administration=== | ||
Epinephrine is supplied as 1 mg/mL (1 mL, 30 mL) which is a 1:1000 solution. | Epinephrine is supplied as 1 mg/mL (1 mL, 30 mL) which is a 1:1000 solution. | ||
The dose for adults with [[immediate hypersensitivity]] reactions is 0.3-0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 ml) every 15-20 minutes. | The dose for adults with [[immediate hypersensitivity]] reactions is 0.3-0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 ml) every 15-20 minutes. Automatic injectors are available for self-administration by patients with known sensitivity. | ||
===Intravenous administration=== | ===Intravenous administration=== | ||
Epinephine is supplied as 0.1 mg/mL (10 mL) which is a 1:10,000 solution. | Epinephine is supplied as 0.1 mg/mL (10 mL) which is a 1:10,000 solution. | ||
The dose for adults during cardiac arrest is 1 mg every 3-5 minutes. | The dose for adults during cardiac arrest is 1 mg every 3-5 minutes. | ||
==Uses== | |||
The uses of epinephrine include treatment of [[anaphylaxis]], [[vasoconstrictor agent]], and [[cardiotonic agent]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 13 August 2024
|
| |||||||
| (-)-epinephrine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | natural hormone | ||||||
| Properties: | |||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Epinephrine (or adrenaline) is a sympathomimetic and catecholamine that is a "active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla in most species. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. It is used in asthma and cardiac failure and to delay absorption of local anesthetics."[1]
Administration
As the dose of epinephrine is sometimes expressed as a ratio only (1 mL of 1:1000) or a concentration only (1 mg in 1 mL), medical errors in administration may be made. [2] This problem is compounded by the availability of 1:1000 and 1:10,000 concentrations for, respectively, subcutaneous and intramuscular, versus intravenous, use.
Subcutaneous and intramuscular administration
Epinephrine is supplied as 1 mg/mL (1 mL, 30 mL) which is a 1:1000 solution. The dose for adults with immediate hypersensitivity reactions is 0.3-0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 ml) every 15-20 minutes. Automatic injectors are available for self-administration by patients with known sensitivity.
Intravenous administration
Epinephine is supplied as 0.1 mg/mL (10 mL) which is a 1:10,000 solution. The dose for adults during cardiac arrest is 1 mg every 3-5 minutes.
Uses
The uses of epinephrine include treatment of anaphylaxis, vasoconstrictor agent, and cardiotonic agent.
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2025), Epinephrine (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Wheeler DW, Carter JJ, Murray LJ, et al (January 2008). "The effect of drug concentration expression on epinephrine dosing errors: a randomized trial". Ann. Intern. Med. 148 (1): 11–4. PMID 18166759. [e]