Homocysteine: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett (New page: {{subpages}} In biochemistry, '''homocysteine''' is a "thiol-containing amino acid formed by a demethylation of methionine.<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> ==References== <references/>) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
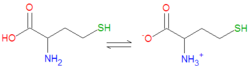
In [[biochemistry]], '''homocysteine''' is a "thiol-containing [[amino acid]] formed by a demethylation of [[methionine]].<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | |||
{{Chem infobox | |||
|align=right | |||
|image={{Image|Homocysteine.png|center|250px|Homocysteine.}} | |||
|width=250px | |||
|molname=homocysteine | |||
|synonyms= | |||
|molformula= C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>9</sub>NO<sub>2</sub>S | |||
|molmass= 135.184760 | |||
|uses=amino acid | |||
|properties=thioated | |||
|hazards=natural compound | |||
|iupac= (2S)-2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid | |||
|casnumber= 6027-13-0 | |||
}} | |||
In [[biochemistry]], '''homocysteine''' is a "thiol-containing [[amino acid]] formed by a demethylation of [[methionine]].<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> It also serves as a chemical precursor of the amino acid [[cysteine]]. | |||
==Role in human disease== | |||
===Homocystinuria=== | |||
{{main|Homocystinuria}} | |||
[[Homocystinuria]] is an "autosomal recessive inborn error of [[methionine]] metabolism usually caused by a deficiency of [[cystathionine beta-synthase]] and associated with elevations of homocysteine in plasma and urine. Clinical features include a tall, slender habitus, [[scoliosis]], [[arachnodactyly]], [[muscle weakness]], [[genu varis]], thin blond hair, malar flush, lens dislocations, an increased incidence of [[mental retardation]], and a tendency to develop fibrosis of arteries, frequently complicated by [[stroke|cerebrovascular accidents]] and [[myocardial infarction]].<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> Homozygous individuals have homocysteine levels that are five times the normal level.<ref name="pmid17124224">{{cite journal |author=Wald DS, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Law M |title=Folic acid, homocysteine, and cardiovascular disease: judging causality in the face of inconclusive trial evidence |journal=BMJ |volume=333 |issue=7578 |pages=1114–7 |year=2006 |month=November |pmid=17124224 |pmc=1661741 |doi=10.1136/bmj.39000.486701.68 |url=http://bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17124224 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
===Hyperhomocysteinemia=== | |||
{{main|Hyperhomocysteinemia}} | |||
[[Hyperhomocysteinemia]] is an "inborn error of [[methionine]] metabolism which produces an excess of homocysteine in the blood. It is often caused by a deficiency of [[cystathionine beta-synthase]] and is a risk factor for [[coronary heart disease|coronary vascular disease]]."<ref>{{MeSH|Hyperhomocysteinemia}}</ref><ref name="OMIM - Hyperhomocysteinemia">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=603174 |title=Homocysteinemia |author= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |format= |work= |publisher=Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= |accessdate=2008-11-16}}</ref> | |||
===Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency=== | |||
About 10% of people are homozygous for the single gene mutation (cytosine is replaced by thymidine at base position 677) that reduces the activity of the enzyme [[methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase]] (MTHFR).<ref name="pmid17124224">{{cite journal |author=Wald DS, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Law M |title=Folic acid, homocysteine, and cardiovascular disease: judging causality in the face of inconclusive trial evidence |journal=BMJ |volume=333 |issue=7578 |pages=1114–7 |year=2006 |month=November |pmid=17124224 |pmc=1661741 |doi=10.1136/bmj.39000.486701.68 |url=http://bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17124224 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid12446535">{{cite journal |author=Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK |title=Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: evidence on causality from a meta-analysis |journal=BMJ |volume=325 |issue=7374 |pages=1202 |year=2002 |month=November |pmid=12446535 |pmc=135491 |doi= |url=http://bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12446535 |issn=}}</ref> These individuals with TT [[genotype]] have a 20% increase in serum homocysteine levels and may have increased [[coronary heart disease]].<ref name="pmid17124224"/><ref name="pmid12446535"/><ref name="OMIM - MTHFR">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=607093 |title=5,10-@methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTHFR|author= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |format= |work= |publisher=Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= |accessdate=2008-11-16}}</ref> | |||
==Treatment to reduce homocysteine levels== | |||
[[Randomized controlled trial]]s have shown the vitamin supplements can lower the homocysteine level; however, this reduction does not lead to reduced mortality<ref name="pmid17848650">{{cite journal |author=Jamison RL, Hartigan P, Kaufman JS, ''et al'' |title=Effect of homocysteine lowering on mortality and vascular disease in advanced chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: a randomized controlled trial |journal=JAMA |volume=298 |issue=10 |pages=1163–70 |year=2007 |month=September |pmid=17848650 |doi=10.1001/jama.298.10.1163 |url=http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17848650 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18714059">{{cite journal |author=Ebbing M, Bleie Ø, Ueland PM, ''et al'' |title=Mortality and cardiovascular events in patients treated with homocysteine-lowering B vitamins after coronary angiography: a randomized controlled trial |journal=JAMA |volume=300 |issue=7 |pages=795–804 |year=2008 |month=August |pmid=18714059 |doi=10.1001/jama.300.7.795 |url=http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18714059 |issn=}}</ref>, reduced [[coronary heart disease]]<ref name="pmid16531614">{{cite journal |author=Bønaa KH, Njølstad I, Ueland PM, ''et al'' |title=Homocysteine lowering and cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=354 |issue=15 |pages=1578–88 |year=2006 |month=April |pmid=16531614 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa055227 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=16531614&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18714059"/> or improved cognition<ref name="pmid16807413">{{cite journal |author=McMahon JA, Green TJ, Skeaff CM, Knight RG, Mann JI, Williams SM |title=A controlled trial of homocysteine lowering and cognitive performance |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=354 |issue=26 |pages=2764–72 |year=2006 |month=June |pmid=16807413 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa054025 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=16807413&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18854539">{{cite journal |author=Aisen PS, Schneider LS, Sano M, ''et al'' |title=High-dose B vitamin supplementation and cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease: a randomized controlled trial |journal=JAMA |volume=300 |issue=15 |pages=1774–83 |year=2008 |month=October |pmid=18854539 |doi=10.1001/jama.300.15.1774 |url=http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18854539 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
A [[meta-analysis]] of these trials by the [[Cochrane Collaboration]] concludes that there is no benefit from lowering the homocysteine level.<ref name="pmid19821378">{{cite journal| author=Martí-Carvajal AJ, Solà I, Lathyris D, Salanti G| title=Homocysteine lowering interventions for preventing cardiovascular events. | journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev | year= 2009 | volume= | issue= 4 | pages= CD006612 | pmid=19821378 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19821378 | doi=10.1002/14651858.CD006612.pub2 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> | |||
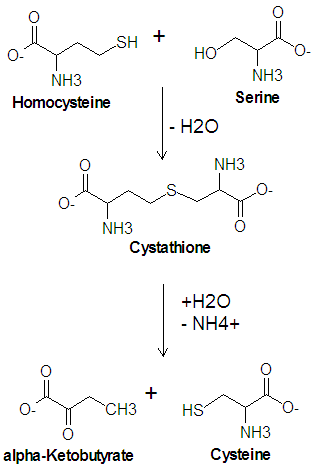
==Biosynthesis of Cysteine from Homocysteine== | |||
{{Image|Cysteine Biosynthesis DEVolk.png|right|350px|Biosynthesis of cysteine from homocysteine, catalyzed by cystathionine synthase and cystathionase.}} | |||
The enzyme [[cystathionine synthase]] catalyzes the condensation reaction of serine with homocysteine producing [[cystathione]] and water. Another enzyme, [[cystathionase]], then catalyzes the [[deamination]] and cleavage of cystathione to produce cysteine and [[alpha-ketobutyrate|<math>\alpha</math>-ketobutyrate]]. In this cleavage reaction, serine acts as the carbon skeleton and homocysteine provides the sulfur atom. | |||
== Synonyms == | |||
Homocysteine is also known by the following synonyms:L-homocysteine; L-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid;(2S)-2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid; 2-amino-4-mercapto-butyric acid; butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-; butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-; butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 29 August 2024
|
| |||||||
| homocysteine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | amino acid | ||||||
| Properties: | thioated | ||||||
| Hazards: | natural compound | ||||||
| |||||||
In biochemistry, homocysteine is a "thiol-containing amino acid formed by a demethylation of methionine.[1] It also serves as a chemical precursor of the amino acid cysteine.
Role in human disease
Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria is an "autosomal recessive inborn error of methionine metabolism usually caused by a deficiency of cystathionine beta-synthase and associated with elevations of homocysteine in plasma and urine. Clinical features include a tall, slender habitus, scoliosis, arachnodactyly, muscle weakness, genu varis, thin blond hair, malar flush, lens dislocations, an increased incidence of mental retardation, and a tendency to develop fibrosis of arteries, frequently complicated by cerebrovascular accidents and myocardial infarction.[2] Homozygous individuals have homocysteine levels that are five times the normal level.[3]
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia is an "inborn error of methionine metabolism which produces an excess of homocysteine in the blood. It is often caused by a deficiency of cystathionine beta-synthase and is a risk factor for coronary vascular disease."[4][5]
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency
About 10% of people are homozygous for the single gene mutation (cytosine is replaced by thymidine at base position 677) that reduces the activity of the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR).[3][6] These individuals with TT genotype have a 20% increase in serum homocysteine levels and may have increased coronary heart disease.[3][6][7]
Treatment to reduce homocysteine levels
Randomized controlled trials have shown the vitamin supplements can lower the homocysteine level; however, this reduction does not lead to reduced mortality[8][9], reduced coronary heart disease[10][9] or improved cognition[11][12]
A meta-analysis of these trials by the Cochrane Collaboration concludes that there is no benefit from lowering the homocysteine level.[13]
Biosynthesis of Cysteine from Homocysteine
The enzyme cystathionine synthase catalyzes the condensation reaction of serine with homocysteine producing cystathione and water. Another enzyme, cystathionase, then catalyzes the deamination and cleavage of cystathione to produce cysteine and -ketobutyrate. In this cleavage reaction, serine acts as the carbon skeleton and homocysteine provides the sulfur atom.
Synonyms
Homocysteine is also known by the following synonyms:L-homocysteine; L-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid;(2S)-2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid; 2-amino-4-mercapto-butyric acid; butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-; butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-; butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-.
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Homocysteine (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Homocysteine (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Wald DS, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Law M (November 2006). "Folic acid, homocysteine, and cardiovascular disease: judging causality in the face of inconclusive trial evidence". BMJ 333 (7578): 1114–7. DOI:10.1136/bmj.39000.486701.68. PMID 17124224. PMC 1661741. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Hyperhomocysteinemia (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Homocysteinemia. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Retrieved on 2008-11-16.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK (November 2002). "Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: evidence on causality from a meta-analysis". BMJ 325 (7374): 1202. PMID 12446535. PMC 135491. [e]
- ↑ 5,10-@methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTHFR. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Retrieved on 2008-11-16.
- ↑ Jamison RL, Hartigan P, Kaufman JS, et al (September 2007). "Effect of homocysteine lowering on mortality and vascular disease in advanced chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA 298 (10): 1163–70. DOI:10.1001/jama.298.10.1163. PMID 17848650. Research Blogging.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Ebbing M, Bleie Ø, Ueland PM, et al (August 2008). "Mortality and cardiovascular events in patients treated with homocysteine-lowering B vitamins after coronary angiography: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA 300 (7): 795–804. DOI:10.1001/jama.300.7.795. PMID 18714059. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Bønaa KH, Njølstad I, Ueland PM, et al (April 2006). "Homocysteine lowering and cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction". N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (15): 1578–88. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa055227. PMID 16531614. Research Blogging.
- ↑ McMahon JA, Green TJ, Skeaff CM, Knight RG, Mann JI, Williams SM (June 2006). "A controlled trial of homocysteine lowering and cognitive performance". N. Engl. J. Med. 354 (26): 2764–72. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa054025. PMID 16807413. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Aisen PS, Schneider LS, Sano M, et al (October 2008). "High-dose B vitamin supplementation and cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA 300 (15): 1774–83. DOI:10.1001/jama.300.15.1774. PMID 18854539. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Martí-Carvajal AJ, Solà I, Lathyris D, Salanti G (2009). "Homocysteine lowering interventions for preventing cardiovascular events.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD006612. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD006612.pub2. PMID 19821378. Research Blogging.