Cefalexin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (New page: {{subpages}}) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Chem infobox | |||
|align=right | |||
|image=[[Image:Cefalexin.png|center|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Cefadroxil.jpg/credit|{{Cefadroxil.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}]] | |||
|width=250px | |||
|molname=cefalexin | |||
|synonyms=cephalexin | |||
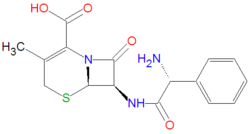
|molformula= C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>17</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S | |||
|molmass= 347.3890 | |||
|uses=antibiotic drug | |||
|properties=beta-lactam | |||
|hazards=see drug interactions | |||
|iupac= see chemistry section | |||
|casnumber=15686-71-2 | |||
}} | |||
'''Cefalexin''' (cephalexin) is one of the most widely used [[antibiotic]] medications. It is a first-generation [[cephalosporin]] type of antibiotic drug, that is sold under nearly 100 brand names. | |||
== Chemistry == | |||
An [[IUPAC]] chemical name of cefalexin is (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula, C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>17</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S, gives it an average molecule mass of 347.3890 gram/mole. Its antibacterial activity is due to the core beta-[[lactam]] structure, which bind with penicillin-binding proteins within bacteria, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, by an acylation reaction of the lactam with the bacterial proteins. | |||
== Brand Names == | |||
{{col-begin|width=100%}} | |||
{{col-break|width=20%}} | |||
* Alcephin | |||
* Alexin | |||
* Alsporin | |||
* Biocef | |||
* Carnosporin | |||
* Cefa-iskia | |||
* Cefablan | |||
* Cefadal | |||
* Cefadin | |||
* Cefadina | |||
* Cefaleksin | |||
* Cefalin | |||
* Cefaloto | |||
* Cefaseptin | |||
* Cefax | |||
* Ceforal | |||
* Cefovit | |||
* Celexin | |||
* Cepastar | |||
* Cepexin | |||
{{col-break|width=20%}} | |||
* Cephacillin | |||
* Cephanasten | |||
* Cephaxin | |||
* Cephin | |||
* Cepol | |||
* Ceporex | |||
* Ceporex Forte | |||
* Ceporexin | |||
* Ceporexin-E | |||
* Ceporexine | |||
* Check | |||
* Cophalexin | |||
* Durantel | |||
* Durantel DS | |||
* Ed A-Ceph | |||
* Erocetin | |||
* Factagard | |||
* Felexin | |||
* Fexin | |||
* Ibilex | |||
{{col-break|width=20%}} | |||
* Ibrexin | |||
* Inphalex | |||
* Kefalospes | |||
* Keflet | |||
* Keflex | |||
* Kefolan | |||
* Keforal | |||
* Keftab | |||
* Kekrinal | |||
* Kidolex | |||
* L-Keflex | |||
* Lafarine | |||
* Larixin | |||
* Lenocef | |||
* Lexibiotico | |||
* Lonflex | |||
* Lopilexin | |||
* Madlexin | |||
* Mamalexin | |||
* Mamlexin | |||
{{col-break|width=20%}} | |||
* Medoxine | |||
* Neokef | |||
* Neolexina | |||
* Novolexin | |||
* Nufex | |||
* Oracef | |||
* Oriphex | |||
* Oroxin | |||
* Ortisporina | |||
* Ospexin | |||
* Palitrex | |||
* Panixine Disperdose | |||
* Pectril | |||
* Pyassan | |||
* Roceph | |||
* Sanaxin | |||
* Sartosona | |||
* Sencephalin | |||
* Sepexin | |||
* Servispor | |||
{{col-break|width=20%}} | |||
* Sialexin | |||
* Sinthecillin | |||
* Sporicef | |||
* Sporidex | |||
* Syncl | |||
* Syncle | |||
* Synecl | |||
* Tepaxin | |||
* Tokiolexin | |||
* Uphalexin | |||
* Voxxim | |||
* Winlex | |||
* Zozarine | |||
{{col-end}} | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 25 July 2024
|
| |||||||
| cefalexin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefalexin (cephalexin) is one of the most widely used antibiotic medications. It is a first-generation cephalosporin type of antibiotic drug, that is sold under nearly 100 brand names.
Chemistry
An IUPAC chemical name of cefalexin is (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula, C16H17N3O4S, gives it an average molecule mass of 347.3890 gram/mole. Its antibacterial activity is due to the core beta-lactam structure, which bind with penicillin-binding proteins within bacteria, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, by an acylation reaction of the lactam with the bacterial proteins.
Brand Names
|
|
|
|
|
References
The most up-to-date information about Cefalexin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cefalexin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefalexin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefalexin - Detailed information from DrugBank.