Ester: Difference between revisions
imported>Simon Overduin m (added some more synthesis information) |
imported>Simon Overduin m (added some more synthesis information) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
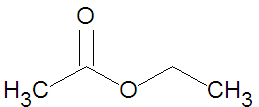
Esters may be formed through a variety of [[esterification]] reactions, most typically the condensation reaction of a [[carboxylic acid]] and an [[alcohol]]<ref name=McMurry1996>McMurry, J. (1996). Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). Scarborough, Ontario: Nelson Canada. pp. 222, 639, 803, 814, 816-817, 823-825.</ref>. For instance, the ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the condensation reaction between [[acetic acid]] and [[ethanol]]. A second method of ester preparation ([[ | Esters may be formed through a variety of [[esterification]] reactions, most typically the condensation reaction of a [[carboxylic acid]] and an [[alcohol]]<ref name=McMurry1996>McMurry, J. (1996). Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). Scarborough, Ontario: Nelson Canada. pp. 222, 639, 803, 814, 816-817, 823-825.</ref>. For instance, the ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the condensation reaction between [[acetic acid]] and [[ethanol]]. A second method of ester preparation ([[alcoholysis]]) uses an acid chloride instead of a carboxylic acid. | ||
Both methods involve [[nucleophilic acyl substitution]], that is, the replacement of one [[nucleophile]] attached to a [[carbonyl]] group with a superior nucleophile<ref name=McMurry1996 />. In | Both methods involve [[nucleophilic acyl substitution]], that is, the replacement of one [[nucleophile]] attached to a [[carbonyl]] group with a superior nucleophile<ref name=McMurry1996 />. In alcoholysis, the leaving nucleophile is a [[halide]] rather than a [[hydroxyl]] group. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 5 March 2008
In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality attached to an alkoxide.
Esters are widely used in the food industry as artificial flavors. Small esters can be used as solvents.
Synthesis
Esters may be formed through a variety of esterification reactions, most typically the condensation reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol[1]. For instance, the ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the condensation reaction between acetic acid and ethanol. A second method of ester preparation (alcoholysis) uses an acid chloride instead of a carboxylic acid.
Both methods involve nucleophilic acyl substitution, that is, the replacement of one nucleophile attached to a carbonyl group with a superior nucleophile[1]. In alcoholysis, the leaving nucleophile is a halide rather than a hydroxyl group.