Supply and demand/Tutorials: Difference between revisions
imported>Nick Gardner |
imported>Nick Gardner |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
that is often used for teaching purposes (with the labels reversed, | that is often used for teaching purposes (with the labels reversed, | ||
unfortunately) | unfortunately). As it stands it adds nothing to Marshall's simple | ||
statement, but it is used as an introduction to the use of such | |||
diagrams to illustrate the concepts of consumer's and supplier's | |||
surplus, and to demonstrate the impact upon them of taxes and subsidies | |||
- | - | ||
Revision as of 04:38, 27 April 2008
(Introduction to be added)
Graphical representations of supply and demand
The shape of the demand curve
The converse of the premise stated in the article is that the less of a thing that a person possesses, the more he is prepared to pay to acquire a little more of it. That means that, as price is increased, a progressively larger increase is needed to produce a given reduction in demand. Thus the slope of the price/demand curve increases as price is increased and falls as price is reduced - leading to a curve that is concave when viewed from above.
-
The basic diagram
This is the stylised representation of the law of supply and demand
that is often used for teaching purposes (with the labels reversed,
unfortunately). As it stands it adds nothing to Marshall's simple
statement, but it is used as an introduction to the use of such
diagrams to illustrate the concepts of consumer's and supplier's
surplus, and to demonstrate the impact upon them of taxes and subsidies
-
-
-
-
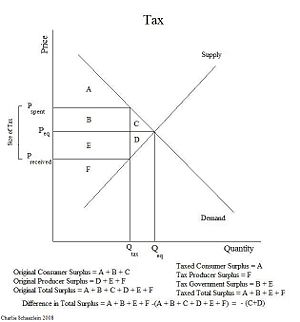
Consumers surplus and the effect of tax
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-