File Transfer Protocol: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Daniel Mietchen (+image) |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
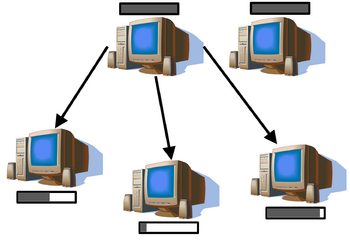
{{Image|File-sharing-via-ftp.png|right|350px|[[File sharing]] via FTP uses a [[host (computing)|host]] from which a dataset (grey filled black box) is being obtained by other computers.}} | {{Image|File-sharing-via-ftp.png|right|350px|[[File sharing]] via FTP uses a [[host (computing)|host]] from which a dataset (grey filled black box) is being obtained by other computers.}} | ||
[[File Transfer Protocol]], or FTP as it is most commonly known, is a protocol specification for the transferring of files between two nodes on an [[Internet Protocol]] network, independent of the [[ | [[File Transfer Protocol]], or FTP as it is most commonly known, is a protocol specification for the transferring of files between two nodes on an [[Internet Protocol]] network, independent of the [[operating system]]. | ||
It is on the [[Application Layer]] of the TCP/IP model. | It is on the [[Application Layer]] of the TCP/IP model. The term has also come to refer to the act of transferring a file using this protocol. A number of software applications facilitate transferring files using FTP. | ||
==Basic protocol== | |||
FTP runs over the [[Transmission Control Protocol]], creating two connections, one for control and one for the actual file transfer. The well-known server ports for the two functions, respectively, are 20 and 21, although the protocol allows both the port number and server IP address to be redirected using the PORT command. | |||
Revision as of 12:33, 17 April 2010

(CC) Image: Langille and Eisen, 2010
File sharing via FTP uses a host from which a dataset (grey filled black box) is being obtained by other computers.
File sharing via FTP uses a host from which a dataset (grey filled black box) is being obtained by other computers.
File Transfer Protocol, or FTP as it is most commonly known, is a protocol specification for the transferring of files between two nodes on an Internet Protocol network, independent of the operating system.
It is on the Application Layer of the TCP/IP model. The term has also come to refer to the act of transferring a file using this protocol. A number of software applications facilitate transferring files using FTP.
Basic protocol
FTP runs over the Transmission Control Protocol, creating two connections, one for control and one for the actual file transfer. The well-known server ports for the two functions, respectively, are 20 and 21, although the protocol allows both the port number and server IP address to be redirected using the PORT command.