Aromatase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
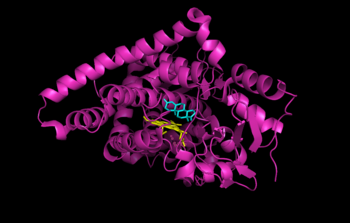
{{Image|Aromatase CytP450 with androstenedione.png|right|350px|Human placental aromatase bound to ligands [[androstenedione]] (cyan) and [[heme]] (yellow). Coordinates obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (3EQM). | {{Image|Aromatase CytP450 with androstenedione.png|right|350px|Human placental aromatase bound to ligands [[androstenedione]] (cyan) and [[heme]] (yellow). Coordinates obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (3EQM).}} | ||
'''Aromatase''' is an [[enzyme]] that removes the C-19 methyl group and oxidizes the 3- and 17-positions of steroids, including reactions that convert androgenic steroids (testosterone) into estrogenic steroids (estrogen). Because some tumors are estrogen-sensitive, [[aromatase inhibitor]]s are sometimes used to treat cancer, mostly in post-menopausal women because aromatase inhibitors do not block estrogen synthesis in the ovaries. | '''Aromatase''' is an [[enzyme]] that removes the C-19 methyl group and oxidizes the 3- and 17-positions of steroids, including reactions that convert androgenic steroids (testosterone) into estrogenic steroids (estrogen). Because some tumors are estrogen-sensitive, [[aromatase inhibitor]]s are sometimes used to treat cancer, mostly in post-menopausal women because aromatase inhibitors do not block estrogen synthesis in the ovaries. | ||
The structure of human placental aromatase cytochrome P450 bound to ligands [[androstenedione]] (cyan) and [[heme]] (yellow) was determined by [[x-ray crystallography]].<ref>{{cite journal|authors = Ghosh, D., Griswold, J., Erman, M. and Pangborn, W.|journal=Nature|volume=457|year=2009|pages=219-225|title=Structural Basis for Androgen Specificity and Estrogen Synthesis in Human Aromatase}}</ref> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 31 May 2009

(CC) Image: David E. Volk
Human placental aromatase bound to ligands androstenedione (cyan) and heme (yellow). Coordinates obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (3EQM).
Human placental aromatase bound to ligands androstenedione (cyan) and heme (yellow). Coordinates obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (3EQM).
Aromatase is an enzyme that removes the C-19 methyl group and oxidizes the 3- and 17-positions of steroids, including reactions that convert androgenic steroids (testosterone) into estrogenic steroids (estrogen). Because some tumors are estrogen-sensitive, aromatase inhibitors are sometimes used to treat cancer, mostly in post-menopausal women because aromatase inhibitors do not block estrogen synthesis in the ovaries.
The structure of human placental aromatase cytochrome P450 bound to ligands androstenedione (cyan) and heme (yellow) was determined by x-ray crystallography.[1]
References
</references>
- ↑ (2009) "Structural Basis for Androgen Specificity and Estrogen Synthesis in Human Aromatase". Nature 457: 219-225.