Acebutolol: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
== General References == | |||
{{CZMed}} | |||
Revision as of 13:53, 4 July 2009
|
| |||||||
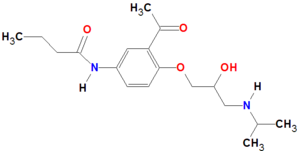
| acebutolol | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | hypertention;angina pectoris | ||||||
| Properties: | |||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Acebutolol is a cardioselective, beta-adrenergic antagonist (beta blocker) with relatively little effects, at low dosage, on bronchial receptors compared to other beta-blockers such as atenolol and propranolol. Epinephrine typically binds to these same receptors, subsequently raising heart rate and blood pressure, but this action is blocked when beta-blockers such as acebutolol bind to these receptors, thereby interferring with epinephrine binding. Blood pressure is also increased by the release of renin, a hormone produced in the kidneys, which narrows blood vessels. By preventing renin release, acebutolol reduces blood pressure by a second mechanism. [1]
References
General References
The most up-to-date information about Acebutolol and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Acebutolol - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Acebutolol - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Acebutolol - Detailed information from DrugBank.