Inositol: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (New article generated using Special:MetadataForm) |
imported>David E. Volk (stub for letter week) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
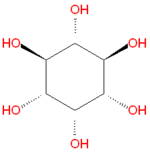
{{Image|Myo-inositol.png|right|150px|Myo-inositol, the most common inositol [[stereoisomer]].}} | |||
'''Inositol''' refers to a collection [[hexose]] [[carbohydrate]]s based on a central [[cyclohexane]] structure with six [[hydroxy]] (OH) groups. Although myo-inositol, previously called meso-inositol, is the most common version found in nature, a number of other stereoisomeric forms are produced naturally. Inositol acts as a [[fatty acid]] transport by coupling its hydroxyl oxygen atoms with the carboxyl groups of fatty acids. | |||
Revision as of 08:50, 11 March 2011
Inositol refers to a collection hexose carbohydrates based on a central cyclohexane structure with six hydroxy (OH) groups. Although myo-inositol, previously called meso-inositol, is the most common version found in nature, a number of other stereoisomeric forms are produced naturally. Inositol acts as a fatty acid transport by coupling its hydroxyl oxygen atoms with the carboxyl groups of fatty acids.