CZ:Featured article/Current: Difference between revisions
imported>Chunbum Park (→Jimmy Page: Hamburger) |
imported>Chunbum Park (Thylakoid) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== '''[[ | == '''[[Thylakoid]]''' == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
{{Image| | {{Image|Chloroplast.png|right|300px|Schematic of a chloroplast: 1. outer membrane; 2. intermembrane space; 3. inner membrane (1+2+3: envelope); 4. [stroma (aqueous fluid); 5. thylakoid lumen (inside of thylakoid); 6. thylakoid membrane; 7. granum (stack of thylakoids); 8. thylakoid (lamella); 9. Starch; 10. Ribosome; 11. plastidial DNA; 12. plastoglobule (drop of lipids).}} | ||
Inside [[plant]] [[Cell (biology)|cells]] and other [[Eukaryote|eukaryotic]] cells that perform [[photosynthesis]], tiny, [[bacteria]]-sized [[organelle]]s, called [[chloroplast]]s, contain, within the inner membrane of their dual membrane structure, an extensive system of single-membrane-bound flattened sacs called '''thylakoids''', their interior spaces (lumens) interconnected, their membranes housing the pigment molecules that absorb the [[energy]] of [[photon]]s of particular frequencies emitted by the sun, an event that initiates the physico-chemical sequence of steps culminating in the products of photosynthesis.<ref>[http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/C/Chloroplasts.html Chloroplasts]. | Additional information about chloroplasts and thylakoids.</ref> A semifluid matrix within the chloroplasts, called the [[stroma]], bathes the thylakoids. The flattened thylakoid sacs consist of clustered stacks, called [[granum|grana]], their lumens interconnected by extensions, called 'stromal thylakoids', or [[lamellae]].<ref name=mustardytpc2008>Mustardy L, Buttle K, Steinbach G, Garab G. (2008) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2590735/?tool=pmcentrez The three-dimensional network of the thylakoid membranes in plants: quasihelical model of the granum-stroma assembly]. ''Plant Cell'' 20:2552-7. | |||
*<font face=Gill Sans MT">View also the supplementary figures and video linked in this paper.</font></ref> [See accompanying illustration at right.] | |||
''[[Thylakoid|.... (read more)]]'' | |||
''[[ | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;" | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" style="width: 90%; float: center; margin: 0.5em 1em 0.8em 0px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: center;" | [[ | ! style="text-align: center;" | [[Thylakoid#References|notes]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 01:33, 2 February 2014
Thylakoid
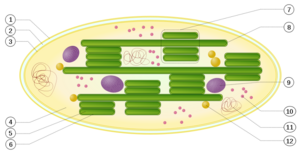
Schematic of a chloroplast: 1. outer membrane; 2. intermembrane space; 3. inner membrane (1+2+3: envelope); 4. [stroma (aqueous fluid); 5. thylakoid lumen (inside of thylakoid); 6. thylakoid membrane; 7. granum (stack of thylakoids); 8. thylakoid (lamella); 9. Starch; 10. Ribosome; 11. plastidial DNA; 12. plastoglobule (drop of lipids).
Inside plant cells and other eukaryotic cells that perform photosynthesis, tiny, bacteria-sized organelles, called chloroplasts, contain, within the inner membrane of their dual membrane structure, an extensive system of single-membrane-bound flattened sacs called thylakoids, their interior spaces (lumens) interconnected, their membranes housing the pigment molecules that absorb the energy of photons of particular frequencies emitted by the sun, an event that initiates the physico-chemical sequence of steps culminating in the products of photosynthesis.[1] A semifluid matrix within the chloroplasts, called the stroma, bathes the thylakoids. The flattened thylakoid sacs consist of clustered stacks, called grana, their lumens interconnected by extensions, called 'stromal thylakoids', or lamellae.[2] [See accompanying illustration at right.]
| notes |
|---|
|