Obesogenic environment: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Gareth Leng |
imported>Ro Thorpe m (moved The Obesogenic Environment to The obesogenic environment) |
Revision as of 18:12, 13 September 2011
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is 01 April 2012. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
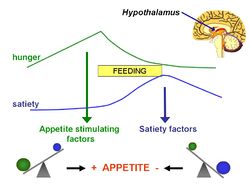
The obesogenic environment encompasses the environmental features of modern lifestyles that are postulated to contribute to the increasing prevalence of obesity; in particular, it is thought that the wide availability of food that is energy dense, palatable and inexpensive, combined with increasingly sedentary habits, favour an excess of energy intake over expenditure.[1]
References
- ↑ Chaput JP et al. (2011) Modern sedentary activities promote overconsumption of food in our current obesogenic environment Obes Rev 12:e12-20 PMID 20576006