Ganges River: Difference between revisions
imported>Pradyumna Singh No edit summary |
imported>Pradyumna Singh No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| 9_data = [[Bay of Bengal]] | | 9_data = [[Bay of Bengal]] | ||
| | | 20_label = Length | ||
| | | 20_data = 2,525 km | ||
| | | 21_label = Left Tributaries | ||
| | | 21_data = Mahakhali, Karnali, Kosi, Gandak, Ghaghra | ||
| | | 22_label = Right Tributaries | ||
| | | 22_data = Yamuna, Son, Mahananda | ||
| | | 23_label = Basin | ||
| | | 23_data = 896,000 sq.km | ||
| 23_label = Discharge | |||
| 23_data = 14,270 cu.m/sec | |||
| 30_label = Ganga | |||
| 30_data = --- | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 19 November 2014
| Ganga | |
|---|---|
| A major river of India | |
| General | |
| Country | India |
| States | Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, |
| Cities | Haridwar, Kanpur, Allahabad, Varanasi, Kolkata |
| Source | Gangotri Glacier, Uttarakhand, India, |
| Mouth | Bay of Bengal |
| Length | 2,525 km |
| Left Tributaries | Mahakhali, Karnali, Kosi, Gandak, Ghaghra |
| Right Tributaries | Yamuna, Son, Mahananda |
| Discharge | 14,270 cu.m/sec |
| Ganga | |
Article Authors : P.Singh
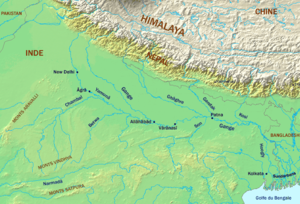
Ganga, official name "Ganga/Ganges"[1], (archaic Ganges) is a major river system in the Indian subcontinent flowing East through North India's Gangetic plains, traversing 2,525 km in the course to discharge into the Bay of Bengal through its vast delta in the Sunderbans and Bangladesh. Several important tributaries add their waters during this journey to make Ganga the 3rd largest river in the world by discharge volume.
The Ganga river basin is India's largest, irrigating the Northern states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal. Important Indian cities on its banks include Kanpur, Patna, Kannauj, Kashi, Allahabad, Varanasi, Kolkata.
Course of the Ganga
Sequence of tributary confluence
Alaknanda joins Dhauliganga (at Vishnuprayag), Mandakini (at Nandprayag), Pindar (at Karnaprayag), Mandakini (at Rudraprayag) and ultimately Bhagirathi (at Devaprayag) from where onwards, it is known as Ganga. The Bhagirathi is considered the prime source stream, fed by melting glacial snow and ice from peaks such as Kamet and Nanda Devi.
Ganga in Indian Religion
Ganga in Hinduism
The river Ganga is generally regarded, since ancient times, amongst the world's most important and holy rivers. It is held sacred by Indians, especially Hindus, and is also worshiped in its anthropomorphic form as the Goddess Ganga, emerging, from Bhagirathi her source, at Gangotri Glacier (in the Central Himalayan state of Uttarakhand) at Gaumukh (elevation 3,892 m). Ganga is embodied at Devprayag when the rampant Alaknanda joins swirling Bhagirathi. Numerous other streams join Himalayan Ganga, among these Mandakini, Dhauliganga, Bhilangana and Pindar are significant.
Ganges in West Bengal
The sanctity of Ganga of Ganga in Bengal predates the arrival of Indo-Aryans. After their arrival and association of Ganga river with Aryan purity, important places of pilgrimage came up at Nawadeep, Triveni, Katwa, Ganga Sagar and Kalighat (near Kolkatta).
Ganga in Islam
Leading Islamic clerics in India have agreed that it is the duty of both Hindus and Muslim to protect and save Ganga, a national river, as both communities live on its banks and earn livelihood from it.[2]
Ganga in Bangladesh
The portions of the eastern sub-delta of the Ganga is known as Padma and had no religious significance or historical places of pilgrimage for Indians unlike in West Bengal along the banks of the Bhagirathi-Hooghly section known a Adi Ganga. The eastern deltaic portions mainly in Bangladesh were always cut off symbolically from Indo-Aryan culture and mythology.[3]


