U.S. Demographic History: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "North Carolina" to "North Carolina (U.S. state)") |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Pennsylvania" to "Pennsylvania") |
||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
!align=“center”|[[New Jersey (U.S. state)|New Jersey]]|| 139,600 || 93,800 || 51,400 || 29,800 || 14,000 || 3,400 || - || - || - | !align=“center”|[[New Jersey (U.S. state)|New Jersey]]|| 139,600 || 93,800 || 51,400 || 29,800 || 14,000 || 3,400 || - || - || - | ||
|- | |- | ||
!align=“center”|[[Pennsylvania]]|| 327,300 || 183,700 || 85,600 || 31,000 || 18,000 || 700 || - || - || - | !align=“center”|[[Pennsylvania (U.S. state)|Pennsylvania]]|| 327,300 || 183,700 || 85,600 || 31,000 || 18,000 || 700 || - || - || - | ||
|- | |- | ||
!align=“center”|[[Delaware (U.S. state)|Delaware]] || 45,400 || 33,300 || 19,900 || 5,400 || 2,500 || 1,000 || 500 || - || - | !align=“center”|[[Delaware (U.S. state)|Delaware]] || 45,400 || 33,300 || 19,900 || 5,400 || 2,500 || 1,000 || 500 || - || - | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 5 August 2023
The Demographic history of the U.S. covers population growth, geographical distribution by states and urban-rural, internal migration, and components of change (births, deaths, immigration), as well as race and ethnicity, and population policy.
Conditions in 2007
The American population has grown steadily to 300 million in 2006 from the 3.9 million were counted in the first census of 1790. However, the annual percentage rate of growth in has shown a nearly continuous decline. The growth has resulted primarily from “natural increase” (more births than deaths) but immigration has played an increasingly important role in recent decades with the origins of immigrants having shifted from Europe to Mexico, Central America, and Asia in recent decades. The most rapid population growth in the United States in recent decades has been in the West and South with slower growth occurring in the Northeast and Midwest. Five western and southern states--California, Florida, Texas, Arizona and Nevada--were the major centers of growth since the 1970s.
The population of the United States is aging, though not as fast as Western Europe and Japan. The median age in the United States was nearly 36 in 2003 compared to about 23 in 1900 and is projected to be more than 40 by 2050. More male than female babies are born, but because of lower mortality rates among females, they come to outnumber males between the ages of 20 to 30 and by the elderly ages the number of females is nearly double that of the number of males. The population is becoming increasingly racially and ethnically diverse. Growth among Hispanic, Asian and black is substantially greater than among whites or Anglos. Hispanics totaled 44.3 million in 2006 -- 14.8 percent of the total population, followed by Blacks at 40.2 million and Asians at 14.9 million. In total ethnic minorities passed the 100 million mark in 2006 (out of 300 million total).[1] Minority populations (have a much lower level of access to socioeconomic resources, such as education and savings, and smaller resource bases than majority groups.[2] The most dramatic impact has been on the public schools. In 1972, 78% of the pupils were white, 15% black, and 7% Hispanic and other. In 2005, 58% were white, 16% black, 20% Hispanic, and 7% Asian and other. In the West, the proportion white fell to 46% in 2005 from 73% in 1972.[3]
Families are changing rapidly. The proportion of married-couple households is declining relative to nontraditional household forms, with heated debates underway about the legal status of same-sex marriages. With the decrease in married-couple households, the high rate of divorce (about 50%), and higher ages at first marriage, the size of households has declined substantially with one- and two-person households now accounting for a majority of all households.
Jobs are changing as well. Farming has shrunk to under 1%, while the rust belt had mile after mile of closed factories. With rapidly rising educational levels, the new jobs are opening in technical fields. The shortage of highly trained engineers has attracted hundreds of thousands of well educated engineers and scientists from around the world. Less skilled jobs are plentiful in areas such as restaurants and construction, where less educated immigrants congregate. Although wages are stagnant for blue collar workers, a steady increase in incomes and wealth holding on the part of the upper middle class, augmented by sky-high incomes for celebrities and CEOs, has increased the level of income inequality. [4]
Census Totals and Estimates
| Historical populations | |
|---|---|
| Census year |
Population |
| 1630 | 4,600 |
| 1650 | 50,400 |
| 1670 | 111,900 |
| 1690 | 210,400 |
| 1700 | 250,900 |
| 1720 | 466,200 |
| 1740 | 905,600 |
| 1750 | 1,170,800 |
| 1770 | 2,148,100 |
| 1780 | 2,780,400 |
| 1790 | 3,929,214 |
| 1810 | 7,239,881 |
| 1820 | 9,638,453 |
| 1830 | 12,866,020 |
| 1840 | 17,069,453 |
| 1850 | 23,191,876 |
| 1860 | 31,443,321 |
| 1870 | 38,558,371 |
| 1890 | 62,979,766 |
| 1900 | 76,212,168 |
| 1910 | 92,228,496 |
| 1920 | 106,021,537 |
| 1930 | 123,202,624 |
| 1940 | 132,164,569 |
| 1950 | 151,325,798 |
| 1960 | 179,323,175 |
| 1970 | 203,211,926 |
| 1980 | 226,545,805 |
| 1990 | 248,709,873 |
| 2000 | 281,421,906 |
| 2007 | 301,139,947 |
| 2010 | 309,162,581 |
| 2020 | 336,031,546 |
| 2030 | 363,811,435 |
| 2040 | 392,172,658 |
| 2050 | 420,080,587 |
Population Growth Patterns
Projections
- 2000 282,338,631
- 2010 309,162,581
- 2020 336,031,546
- 2030 363,811,435
- 2040 392,172,658
- 2050 420,080,587
- 2060 450,505,985
- 2070 480,568,004
- 2080 511,442,859
- 2090 540,405,985
- 2100 571,440,474
public
Regional Trends
Marriage and fertility
In Plymouth Plantation in the 17th century, a fairly comprehensive demographic study was done by historian John Demos for his 1970 work A Little Commonwealth. He reports that the size of the average household size grew as time passed in Plymouth colony, with the average of 7.8 children per family for first-generation families, 8.6 children for second-generation families, and 9.3 for third-generation families. Child mortality also decreased over this time, with 7.2 children born to first-generation families living until their 21st birthday. The number increased to 7.9 children by the third generation.[5]
Mortality
In Plymouth Plantation in the 17th century, life expectancy was higher for men than for women. Of the men who survived until the age of 21, the average life expediency was 69.2 years. Over 55 percent of these men lived past 70, less than 15 percent died before the age of 50. For women, the numbers are much lower, owing to the difficulties inherent in childbirth. The average life expediency of women at the age of 21 was only 62.4 years. Of these women, less than 45 percent lived past 70, and about 30 percent died before the age of 50.[6]
Infant Mortality
see Infant mortality
Demographic transition
See also Demographic transition
Greenwood and Seshadri (2002) show that from 1800 to 1940 there was a demographic shift from a mostly rural US population with high fertility, with an average of seven children born per white woman, to a minority (43%) rural population with low fertility, with an average of two births per white woman. This shift resulted from technological progress. A sixfold increase in real wages made children more expensive in terms of forgone opportunities to work and increases in agricultural productivity reduced rural demand for labor, a substantial portion of which traditionally had been performed by children in farm families.[7]
Morbidity and Disease
Malaria
Tuberculosis
Heart Disease
Infectious Disease
HIV-AIDS
Age Distribution
Old Age
Welfare Ratios
Social Security and Medicare
Population projections
The US population in 1900 was 76 million. In 1950, it rose to 152 million by 2000 it had reached 282 million. By 2050, 420 million and then 571 million by 2100.
Urban - Rural Distributions
Internal Migration
Rural flight is the departure of excess populations (usually young men and women) from farm areas. In some cases whole families left, as in the Dust Bowl in the 1930s. Much of rural America has seen steady population decline since 1920.
Black Migration out of South
see Great Migration (African American) The Great Migration was the movement of millions African Americans out of the rural Southern United States from 1914 to 1960. Most moved to large industrial cities, as well as to many smaller industrial cities. African-Americans moved as individuals or small groups. There was no government assistance. They migrated because of a variety of push and pull factors:
Push factors
- Many African-Americans wanted to avoid the racial segregation of the Jim Crow South and sought refuge in the supposed "Promised Land" of the North where there was thought to be less segregation
- The boll weevil infestation of the cotton fields of the South in the late 1910s, reduced the demand for sharecroppers.
- The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 and its aftermath displaced hundreds of thousands of African-American farm workers;
Pull factors
- Income levels were much higher in the North, with far higher wages in the service sector.
- The enormous growth of war industries in WW1 and WW2 created new job openings for blacks—not in the factories but in the service jobs that new factory workers vacated;
- World War I effectively put a halt to the flow of European immigrants to the great industrial centers of the Northeast and Midwest, causing shortages of workers in the factories.
- In the 1930s WPA, CCC and other relief programs in the North were more receptive to blacks. The WPA paid more in the North.
- After 1940, as the U.S. rearmed for World War II (see Homefront-United States-World War II), industrial production increased rapidly in every region.
- The FEPC equal opportunity laws were more enforced in the North and West.[8]
Immigration
Colonial Era
The extent of colonial settlements by 1800 is shown by this map from the reatUniversity of Texas map collection. [1]
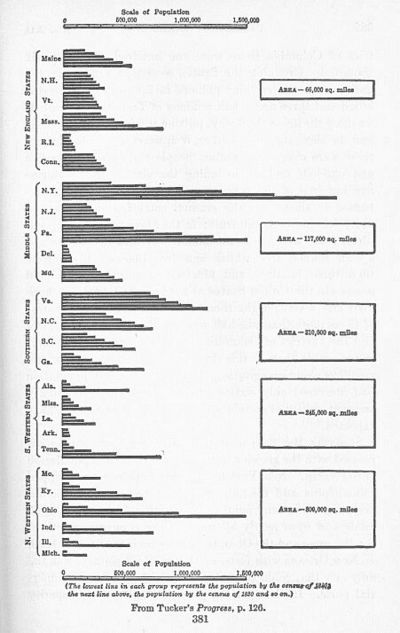
| Estimated Population of American Colonies 1620 to 1780 Series Z-19 U.S. Census | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1780 | 1760 | 1740 | 1720 | 1700 | 1680 | 1660 | 1640 | 1620 |
| Tot Pop. | 2,780,400 | 1,593,600 | 905,600 | 466,200 | 250,900 | 151,500 | 75,100 | 26,600 | 500 |
| Maine -1 | 49,100 | 20,000 | - | - | - | - | - | 900 | - |
| New Hampshire-2 | 87,800 | 39,100 | 23,300 | 9,400 | 5,000 | 2,000 | 1,600 | 1,100 | - |
| Vermont -3 | 47,600 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Plymouth -4 | - | - | - | - | - | 6,400 | 2,000 | 1,000 | 100 |
| Massachusetts | 268,600 | 202,600 | 151,600 | 91,000 | 55,900 | 39,800 | 20,100 | 8,900 | |
| Rhode Island | 52,900 | 45,500 | 25,300 | 11,700 | 5,900 | 3,000 | 1,500 | 300 | - |
| Connecticut | 206,700 | 142,500 | 89,600 | 58,800 | 26,000 | 17,200 | 8,000 | 1,500 | - |
| New York | 210,500 | 117,100 | 63,700 | 36,900 | 19,100 | 9,800 | 4,900 | 1,900 | - |
| New Jersey | 139,600 | 93,800 | 51,400 | 29,800 | 14,000 | 3,400 | - | - | - |
| Pennsylvania | 327,300 | 183,700 | 85,600 | 31,000 | 18,000 | 700 | - | - | - |
| Delaware | 45,400 | 33,300 | 19,900 | 5,400 | 2,500 | 1,000 | 500 | - | - |
| Maryland | 245,500 | 162,300 | 116,100 | 66,100 | 29,600 | 17,900 | 8,400 | 500 | - |
| Virginia | 538,000 | 339,700 | 180,400 | 87,800 | 58,600 | 43,600 | 27,000 | 10,400 | 400 |
| North Carolina (U.S. state) | 270,100 | 110,400 | 51,800 | 21,300 | 10,700 | 5,400 | 1,000 | - | - |
| South Carolina | 180,000 | 94,100 | 45,000 | 17,000 | 5,700 | 1,200 | - | - | - |
| Georgia | 56,100 | 9,600 | 2,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kentucky | 45,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tennessee | 10,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Year | 1780 | 1760 | 1740 | 1720 | 1700 | 1680 | 1660 | 1640 | 1620 |
| New Eng. (ME to CT) | 712,800 | 449,600 | 289,700 | 170,900 | 92,800 | 68,500 | 33,200 | 13,700 | 100 |
| % Black -5 | 2.0% | 2.8% | 2.9% | 2.3% | 1.8% | 0.7% | 1.8% | 1.5% | 0.0% |
| Middle (NY to DE) | 722,900 | 427,900 | 220,600 | 103,100 | 53,600 | 14,900 | 5,400 | 1,900 | - |
| % Black -6 | 5.9% | 6.8% | 7.5% | 10.5% | 6.9% | 10.1% | 11.1% | 10.5% | 0.0% |
| South (MD to TN) | 1,344,700 | 716,000 | 395,300 | 192,300 | 104,600 | 68,100 | 36,400 | 11,000 | 400 |
| % Black -7 | 38.6% | 39.7% | 31.6% | 28.1% | 21.5% | 7.3% | 4.7% | 1.8% | 0.0% |
- Maine was part of Massachusetts until 1820.
- Vermont was disputed between Massachusetts, New York and New Hampshire until the settlers declared their independence from all of them and were accepted as the 14th state in 1791 and participated in the 1790 census a year late.
- Plymouth, Massachusetts, the first permanent New England settlement, in 1690 became part of the Massachusetts colony.
- By 1784 all slavery in the New England states was either completely prohibited or transitioning to its total prohibition.
- By 1804 all slavery in the Middle colonies (except Delaware [6.6% Black]) was either completely prohibited or was transitioning to its total prohibition.
- All slavery was prohibited in the entire U.S. in 1865 by the 13th amendment to the constitution.
Population growth is nearly always by natural increase but significant immigration can sometimes be seen in some states when populations grow by more than 80% {a 3% growth rate) in a 20 year interval.
Population in 1790
The following were the countries of origin for new arrivals coming to the United States before 1790. The regions marked * were part of Great Britain. The ancestry of the 3.9 million population in 1790 has been estimated by various sources by sampling last names in the 1790 census and assigning them a country of origin. The Irish in the 1790 census were mostly Scots Irish. The French were mostly Huguenots. The total U.S. Catholic population in 1790 was probably less than 5%. The Indian population inside territorial U.S. 1790 boundaries was less than 100,000.[9]
| U.S. Historical Populations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Country | Immigrants Before 1790 | Population 1790 -1 |
| Africa -2 | 360,000 | 757,000 |
| England* | 230,000 | 2,100,000 |
| Ulster Scot-Irish* | 135,000 | 300,000 |
| Germany -3 | 103,000 | 270,000 |
| Scotland* | 48,500 | 150,000 |
| Ireland* | 8,000 | (Incl. in Scot-Irish) |
| Netherlands | 6,000 | 100,000 |
| Wales* | 4,000 | 10,000 |
| France | 3,000 | 15,000 |
| Jews -4 | 1,000 | 2,000 |
| Sweden | 500 | 2,000 |
| Other -5 | 50,000 | 200,000 |
| Total -6 | 950,000 | 3,900,000 |
- Data from Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR)
- Jewish settlers were from several European countries.
- The Total is the total immigration over the approximately 130 year span of colonial existence of the U.S. colonies as found in the 1790 census. Many of the colonists, especially from the New England colonies, are already into their fifth generation of being in America. At the time of the American Revolution the foreign born population is estimated to be from 300,000 to 400,000.
The 1790 population already reflects the approximate 50,000 “Loyalists or Tories”, who emigrated to Canada at the end of the American Revolution and the less than 10,000 more who emigrated to other British possessions including England.
Already by 1790 the ancestry question is starting to become meaningless as many people from many different countries intermarry in each generation and nearly all these ancestries are starting to merge to become American. The total white population in 1790 was about 80% British ancestry and roughly doubles by natural increase every 25 years. The native born population of the U.S. has never fallen below 85% of the population after about 1675--100 years before the American Revolution.
Relentless population expansion pushed the U.S. frontier to the Pacific by 1848. Given the U.S. geography, most immigrants came long distances to settle in the U.S.. However the Irish leaving Canada for the US in the 1840s, the French Canadians who came down from Quebec after 1860, and the Mexicans who came north after 1911, found it easy to move back and forth.
Immigration 1790 to 1849
In the early years of the U.S., immigration was only about 6000 people a year on average, including French refugees from the slave revolt in Haiti. The French Revolution, starting in 1789, and the Napoleonic Wars from 1792 to 1814 severely limited immigration from Europe. The War of 1812 (1812-1814) with Britain again prevented any significant immigration. By 1808, Congress had banned the importation of slaves, slowing that human traffic to a trickle. After 1820, immigration gradually increased. For the first time, federal records, including ship passenger lists, were kept for immigration. Total immigration for one year in 1820 was 8,385, gradually building to 23,322 by 1830 with 143,000 total immigrating during the intervening decade. From 1831 to 1840, immigration increased greatly, to 599,000 total, as 207,000 Irish, even before the famine of 1845-49, started to emigrate in large numbers as Britain eased travel restrictions. 152,000 Germans, 76,000 British, and 46,000 French formed the next largest immigrant groups in that decade. From 1841 to 1850, immigration exploded to 1,713,000 total immigrants as at least 781,000 Irish, with the famine of 1845-1919 driving them, fled their homeland to escape poverty and death. The British, attempting to divert some of this traffic to help settle Canada, offered bargain fares of 15 shillings, instead of the normal 5 pounds (100 shillings) for transit to Canada. Thousands of poor Irish took advantage of this offer, and headed to Canada on what came to be called the "coffin ships" because of their high death rates. Once in Canada, many Irish walked across the border or caught an intercoastal freighter to the nearest major city in the United States - usually Boston or New York. Bad potato crops and failed revolutions struck the heart of Europe in 1848, contributing to the decade's total of 435,000 Germans, 267,000 British and 77,000 French immigrants. Bad times in Europe drove people out; land, relatives, freedom, opportunity and jobs in America lured them in.
| Population and Foreign Born 1790 to 1849 Census Population, Immigrants per Decade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Population | Immigrants-1 | Foreign Born | % |
| 1790 | 3,918,000 | 60,000 | ||
| 1800 | 5,236,000 | 60,000 | ||
| 1810 | 7,036,000 | 60,000 | ||
| 1820 | 10,086,000 | 60,000 | ||
| 1830 | 12,785,000 | 143,000 | 200,000 -2 | 1.6% |
| 1840 | 17,018,000 | 599,000 | 800,000 -2 | 4.7% |
| 1850 | 23,054,000 | 1,713,000 | 2,244,000 | 9.7% |
The number of immigrants from 1830 on are from immigration records. The census of 1850 was the first census in which place of birth was asked. It is probably a reasonable estimate that the foreign born population in the U.S. reached its minimum in about 1815 at something like 100,000 or 1.4% of the population. By 1815, most of the immigrants that arrived before the American Revolution had passed on, and there had been almost no new immigration.
- The total number immigrating in each decade from 1790 to 1820 are estimates.
- The number foreign born in 1830 and 1840 decades are extrapolations.
Nearly all population growth up to 1830 was by internal increase; about 98.5% of the population was native-born. By 1850, this had shifted to about 90% native-born. The first large-scale Catholic immigration started in the mid 1840s from Germany and Ireland.
In 1848, following conquest of the Southwest in the Mexican war American citizenship to approximately 60,000 Mexican residents of the New Mexico Territory and 10,000 living in California. In 1849, the California Gold Rush spurred significant immigration from Mexico, South America, China, Australia, Europe and caused a mass migration within the US, resulting in California gaining statehood in 1850, with a population of about 90,000.
Restriction
Ethnic and Racial Structure
European Americans (White)
African Americans (Black)
Native Americans and Pacific Islanders
Asian Americans
Hispanics/Latinos
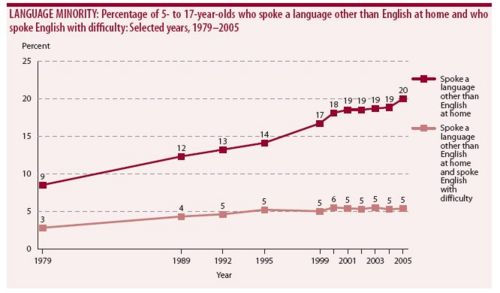
see Latino history The rapid growth of the Hispanic population after 1972 began in the Southwest, but spread nationwide by 2000. In 1972 Hispanics comprised 6% of public school students, and more than tripled to 20% in 2005. However, despite fears that assimilation would be difficult, the proportion of students who spoke English with difficulty has been flat at 5%, according to graph 1.
Population Policies
Natalism
Abortion
Birth Control
Child Health
Demographic models in Historiography
Turner's Frontier Thesis
Easterlin Models
Richard Easterlin is an economist and professor of economics who has researched and published much literature on economic growth in the United States. In one of Richard Easterlin’s articles, published in 2000, titled, Twentieth Century American Population Growth, he explains the growth pattern of American population in the twentieth century by examining the fertility rate fluctuations and the decreasing mortality rate. In his article, Easterlin attempts to prove the cause of the Baby Boom and Baby Bust by the “relative income” theory, despite the various other theories that these events have been attributed to. The “relative income” theory suggests that couples choose to have children based on a couple’s ratio of potential earning power and the desire to obtain material objects. This ratio depends on the economic stability of country and how people are raised to value material objects. The “relative income” theory explains the Baby Boom by suggesting that the late 1940s and 1950s brought low desires to have material objects, because of the Great Depression and WWII, as well as huge job opportunities, because of being a post war period. These two factors gave rise to a high relative income, which encouraged high fertility. Following this period, the next generation had a greater desire for material objects, however, an economic slowdown in the United States, made jobs harder to acquire. This resulted in lower fertility rates causing the Baby Bust.
Epidemiological transition
Demographic Data
Vital registration
Census
Surveys
Online Sources
Historical research
Contemporary Studies
Regional trends
Between, 1880 and 1900, the urban population of the United States rose from 28% to 40% (1), and reached 50% by 1920, in part due to 9,000,000 European immigrants. After 1890, the US rural population began to plummet, as farmers were displaced by mechanization and forced to migrate to urban factory jobs. After World War II, the US experienced a shift away from the cities, mostly due to the gaining popularity of the automobile and heavy government funding of suburban housing and highways. Many of the original manufacturing cities lost as much as half their population between 1950 and 1980. There was a shift in the population from the dense manufacturing centers of the Northeast (rust belt) to the outer suburbs of these cities and to newer, less dense cities in the Southwest (sun belt).
Bibliography
- Barkan, Elliott Robert. From All Points: America's Immigrant West, 1870s-1952, (2007) 598 pages
- Barrett, Richard E., Donald J. Bogue, and Douglas L. Anderton. The Population of the United States (3rd ed. 1997) 704pp; massive compendium of data text search
- Brunner, Edmund de Schweinitz. Rural social trends (1933) online edition
- Carter, Susan B., Scott Sigmund Gartner, Michael R. Haines, and Alan L. Olmstead, eds. The Historical Statistics of the United States (Cambridge UP: 6 vol; 2006) vol 1 on population; available online; massive data compendium; online version in Excel
- Chadwick, Bruce A. and Tim B. Heaton, eds. Statistical Handbook on the American Family. (1992)
- Cramer, Clayton E. Black Demographic Data, 1790-1860: A Sourcebook Greenwood Press, 1997 online edition
- Easterlin, Richard A. Birth and Fortune: The Impact of Numbers on Personal Welfare (1987), by leading economist excerpt and text search
- Ellis, David R. Applied Demography (1991) online edition
- Gillon, Steve. Boomer Nation: The Largest and Richest Generation Ever, and How It Changed America (2004), by leading historian. excerpt and text search
- Gerhan, David R. and Robert V. Wells. A Retrospective Bibliography of American Demographic History from Colonial Times to 1983. (Greenwood Press, 1989)
- Michael R. Haines and Richard H. Steckel (eds.), A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press, 2000, 752 pp. advanced scholarship
- Hawes Joseph M. and Elizabeth I. Nybakken, eds. American Families: a Research Guide and Historical Handbook. (Greenwood Press, 1991)
- Klein, Herbert S. A Population History of the United States. Cambridge University Press, 2004. 316 pp
- Knox, P. L. et al. The United States: A Contemporary Human Geography. Longman, 1988. 287 pp.
- Mintz Steven and Susan Kellogg. Domestic Revolutions: a Social History of American Family Life. (1988)
- Riley, Moffat. Population History of Western U.S. Cities and Towns, 1850-1990 (1996); Population History of Eastern U.S. Cities and Towns, 1790-1870 (1992)
- Pillsbury, Richard, ed. The New Encyclopedia of Southern Culture. Vol. 2: Geography. U. of North Carolina Press, 2006. 248 pp.
- Thompson, Warren Simpson. Population trends in the United States (1933) online edition
- U.S. Bureau of the Census, Historical Statistics of the United States: Colonial Times to 1970 (1976)
- Wells, Robert V. Revolutions in Americans' Lives: A Demographic Perspective on the History of Americans, Their Families, and Their Society (1982)
- Wells, Robert V. Uncle Sam's Family (1985), general demographic history
Primary sources
- Kennedy, Joseph C. G. Population of the United States in 1860 (1864) official returns of 8th censuscomplete text online
External links
- City Ranks is an interactive map showing population densities of US cities]
- World Population: A Guide to the Web
see also
notes
- ↑ See Census press release at [2]
- ↑ Asians, especially recent immigrants from China and India, have higher levels of education and income.
- ↑ See NCES, The Condition of Education 2007 (2007) at [3]
- ↑ David R. Ellis, Applied Demography (1991) p. 66-67.
- ↑ Demos (1970), Appendices, pp 192-194
- ↑ Demos A Little Commonwealth 1970
- ↑ Jeremy Greenwood, and Seshadri, Ananth. "The U.S. Demographic Transition." American Economic Review (2002) 92(2): 153-159. Issn: 0002-8282 Fulltext: Jstor
- ↑ Grossman, James R. Land of Hope: Chicago, Black Southerners, and the Great Migration (1991); Lemann, Nicholas. The Great Black Migration and How It Changed America (1992); and Scott, Emmett J., Negro Migration during the War (1920).
- ↑ The Source: A Guidebook of American Genealogy by Kory L. Meyerink and Loretto Dennis Szucs,