Influenza: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett (→Differential diagnosis: removed from the second list viruses that were in both lists.) |
imported>Robert Badgett |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
===Influenza in humans=== | ===Influenza in humans=== | ||
[[Image:Labsummary06-07.GIF|right|thumb|350px|{{#ifexist:Template:Labsummary06-07.GIF/credit|{{Labsummary06-07.GIF/credit}}<br/>|}}Seasonal influenza activity in the [[United States]] over four years. During the off season, the prevalence is | [[Image:Labsummary06-07.GIF|right|thumb|350px|{{#ifexist:Template:Labsummary06-07.GIF/credit|{{Labsummary06-07.GIF/credit}}<br/>|}}Seasonal influenza activity in the [[United States]] over four years. During the off season, the prevalence is < 2%. During the height of season, the prevalence may be 20-35%.<ref name="titleCDC - Influenza (Flu) | Flu Activity">{{cite web |url=http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/fluactivity.htm |title=Flu Activity |accessdate=2007-11-29 |author=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |format= |work= |publisher= |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote=}}</ref>.]] | ||
The prevalence of influenza among people who have an "influenza-like illness" varies strongly with the seasons of the year. | |||
* During the off season, the the prevalence is < 2%<ref name="titleCDC - Influenza (Flu) | Flu Activity"/> | |||
* During the height of season, the prevalence may be 20-35%.<ref name="titleCDC - Influenza (Flu) | Flu Activity"/> | |||
* During local outbreaks, the prevalence may be 50-80%.<ref name="pmif12361816">{{cite journal | author = Smith K, Roberts M | title = Cost-effectiveness of newer treatment strategies for influenza. | journal = Am J Med | volume = 113 | issue = 4 | pages = 300-7 | year = 2002 | doi = 10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01222-6 | id = PMID 12361816}}</ref><ref name="pimd12965940">{{cite journal | author = Rothberg M, Bellantonio S, Rose D | title = Management of influenza in adults older than 65 years of age: cost-effectiveness of rapid testing and antiviral therapy. | journal = Ann Intern Med | volume = 139 | issue = 5 Pt 1 | pages = 321-9 | year = 2003 | url = http://www.annals.org/cgi/content/abstract/139/5_Part_1/321 | id = PMID 12965940}}</ref> | |||
In addition to seasonal variations, there have been several worldwide influenza [[epidemic]]s, resulting in millions of deaths. | |||
===Equine Influenza=== | ===Equine Influenza=== | ||
Revision as of 13:46, 29 November 2007
Influenza, commonly called “the ‘Flu”, is a common viral infectious disease. That means that It is contagious (easily passed from one person to another) and is caused by viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family.
Epidemiology
Influenza in humans
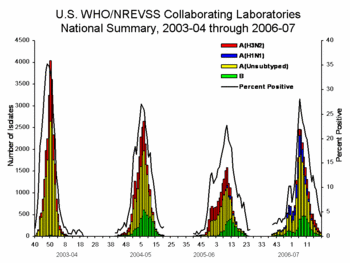
The prevalence of influenza among people who have an "influenza-like illness" varies strongly with the seasons of the year.
- During the off season, the the prevalence is < 2%[1]
- During the height of season, the prevalence may be 20-35%.[1]
- During local outbreaks, the prevalence may be 50-80%.[2][3]
In addition to seasonal variations, there have been several worldwide influenza epidemics, resulting in millions of deaths.
Equine Influenza
This is a species-specific strain that infects horses, ponies, donkeys and mules. Humans do not catch this disease but are carriers of it. It is airborne and highly contagious. Equine influenza generally does not kill its victims, and affected horses display similar symptoms to those of humans.
In 2007, a horse flu epidemic began in New South Wales, Australia. The outbreak is believed to have begun as a result of infractions of proper quarantine procedure and is expected to cost millions of dollars in lost revenue. As of September, 2007, it had spread to the Victorian border, causing the cancellation of events at the Melbourne Show, and the possibility that the Spring Carnival, including the running of the Melbourne Cup horse race, would be canceled.
Avian flu
Avian flu, also known as Bird flu or H5N1, has led to recent outbreaks.[4][5]
Diagnosis
History and physical examination
A systematic review by the Rational Clinical Examination concluded that the best findings for excluding the diagnosis of influenza are:[6]
| Finding: | sensitivity | specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | 86% | 25% |
| Cough | 98% | 23% |
| Nasal congestion | 70–90% | 20–40% |
Notes to table:
- All three findings, especially fever, were less sensitive in patients over 60 years of age.
Since anti-viral drugs are effective in treating influenza if given early (see treatment section, below), it can be important to identify cases early. Of the symptoms listed above, the combinations of findings below can improve diagnostic accuracy.[7] Unfortunately, even combinations of findings are imperfect. However, Bayes Theorem can combine pretest probability with clinical findings to adequately diagnose or exclude influenza in some patients. The pretest probability has a strong seasonal variation; the current prevalence of influenza among patients in the United States receiving sentinel testing is available at the CDC.[8] Using the CDC data, the following table shows how the likelihood of influenza varies with prevalence:
| Combinations of findings | Sensitivity | Specificity | Projected during local outbreaks (prevalence approx 66%[2][3]) |
Projected during influenza season (prevalence=25%) |
Projected in off-season (prevalence=2%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPV | NPV | PPV | NPV | PPV | NPV | |||
| Fever and cough | 64% | 67% | 79% | 49% | 39% | 15% | 4% | 1% |
| Fever and cough and sore throat | 56 | 71 | 79 | 45 | 39 | 17 | 4 | 2 |
| Fever and cough and nasal congestion | 59 | 74 | 81 | 48 | 43 | 16 | 4 | 1 |
Empiric treatment may be justified in the elderly as long as the probability of influenza is over 15%[3] and in other adults if the prevalence is over 30%[2]. Two decision analysis studies[2][3] suggest that during local outbreaks of influenza, the prevalence will be over 70%[3] and thus patients with any of the above combinations of symptoms may be treated with neuramidase inhibitors without testing. In the absence of a local outbreak, treatment may be justified in the elderly during the influenza season as long as the prevalence is over 15%.[3]
Differential diagnosis
Influenza-like illness is defined as "fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat in the absence of a known cause other than influenza."[9] A study from Australia found that possible causes for influenza-like illness include respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, adenovirus, parainfluenza viruses, coronaviruses, and metapneumovirus.[10]
Other diagnoses to consider are:
- Parvovirus B19 - arthropathy is prominent
- Flaviviruses
- Dengue fever - bonebreak fever with retro-orbital pain
- West Nile virus - tremor is common
Treatment
The two classes of anti-virals are neuraminidase inhibitors and M2 inhibitors (adamantane derivatives). Neuraminidase inhibitors are currently preferred for flu virus infections.
Different strains of influenza virus have differing degrees of resistance against these antivirals and it is impossible to predict what degree of resistance a future pandemic strain might have.[11]
When to treat
According to two decision analysis studies, treatment may be justified in the elderly as long as the probability of influenza is over 15%[3] and in other adults if the probability is over 30%[2].
Neuraminidase inhibitors
These drugs are often effective against both influenza A and B.[12] Examples are oseltamivir (trade name Tamiflu) and zanamivir (trade name Relenza) are neuraminidase inhibitors.[13] The Cochrane Collaboration concluded that these drugs reduce symptoms and complications.[14] Zanamivir may cause bronchospasm in patients with asthma.
M2 inhibitors (adamantanes)
These drugs are sometimes effective against influenza A if given early in the infection, but are always ineffective against influenza B. Examples include the antiviral drugs amantadine and rimantadine which block a viral ion channel and prevent the virus from infecting cells. [12]
Prevention
Vaccination
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has published recommendations on who should get the influenza vaccination.[15]
Neuraminidase inhibitors
The Cochrane Collaboration has concluded that neuraminidase inhibitors can prevent symptomatic influenza.[14] Zanamivir may cause bronchospasm in patients with asthma.
History
Spanish influenza pandemic of 1918
A pandemic of Spanish Influenza swept across Europe in the wake of the Great War (1918-19). More people are believed to have died of the flu in the year after the war then in the Great War itself. Estimates vary but it is estimated that one third of the world's population were infected and up to 50 million people perished in this pandemic (it is possibly that fatalities world wide were as high as 100 million).[16] Some comparisons are drawn between Spanish Flu and the Black Death (Bubonic Plague) of 1347 to 1351. Estimates are that the flu killed more people in one year than plague did in four.
In the United States, the epidemic led to closing of schools and banning of public meetings in order to successfully reduce mortality.[17]
External links
- Influenza at CDC
- Influenza at World Health Organization
- Health encyclopedia entry at NHS Direct
- BioHealthBase Bioinformatics Resource Center Database of influenza sequences and related information.
- Overview of influenza at MedicineNet
- Orthomyxoviridae The Universal Virus Database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
- Influenza Virus Resource at the NCBI
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Flu Activity. Retrieved on 2007-11-29.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Smith K, Roberts M (2002). "Cost-effectiveness of newer treatment strategies for influenza.". Am J Med 113 (4): 300-7. DOI:10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01222-6. PMID 12361816. Research Blogging.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Rothberg M, Bellantonio S, Rose D (2003). "Management of influenza in adults older than 65 years of age: cost-effectiveness of rapid testing and antiviral therapy.". Ann Intern Med 139 (5 Pt 1): 321-9. PMID 12965940.
- ↑ Oner AF, Bay A, Arslan S, et al (2006). "Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in eastern Turkey in 2006". N. Engl. J. Med. 355 (21): 2179–85. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa060601. PMID 17124015. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Kandun IN, Wibisono H, Sedyaningsih ER, et al (2006). "Three Indonesian clusters of H5N1 virus infection in 2005". N. Engl. J. Med. 355 (21): 2186–94. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa060930. PMID 17124016. Research Blogging.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Call S, Vollenweider M, Hornung C, Simel D, McKinney W (2005). "Does this patient have influenza?". JAMA 293 (8): 987-97. DOI:10.1001/jama.293.8.987. PMID 15728170. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Monto A, Gravenstein S, Elliott M, Colopy M, Schweinle J (2000). "Clinical signs and symptoms predicting influenza infection.". Arch Intern Med 160 (21): 3243–7. PMID 11088084.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Accessed January 1, 2007.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2007). CDC - Influenza (Flu) - Flu Activity. Retrieved on 2007-11-19.
- ↑ Kelly H, Birch C (2004). "The causes and diagnosis of influenza-like illness". Australian family physician 33 (5): 305–9. PMID 15227858. [e]
- ↑ Webster, Robert G. (2006). "H5N1 Influenza — Continuing Evolution and Spread". N Engl J Med 355 (21): 2174–77. PMID 16192481.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Stephenson, I; Nicholson K (1999). "Chemotherapeutic control of influenza". J Antimicrob Chemother 44 (1): 6–10. PMID 10459804.
- ↑ Moscona, A (2005). "Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza". N Engl J Med 353 (13): 1363–73. PMID 16192481.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Jefferson, T; Demicheli V, Di Pietrantonj C, Jones M, Rivetti D. "Neuraminidase inhibitors for preventing and treating influenza in healthy adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3: CD001265. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD001265.pub2. PMID 16855962. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC - Influenza (Flu): Vaccination. Retrieved on 2007-11-29.
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol12no01/05-0979.htm
- ↑ Markel H, Lipman HB, Navarro JA, et al (2007). "Nonpharmaceutical interventions implemented by US cities during the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic". JAMA 298 (6): 644–54. DOI:10.1001/jama.298.6.644. PMID 17684187. Research Blogging.