Aspartic acid: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (stub and structure) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
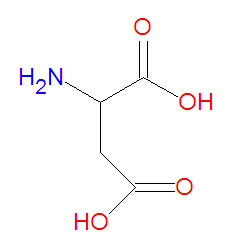
[[Image:Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg|right|thumb|350px|{{#ifexist:Template:Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg/credit|{{Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}'''Aspartic acid''', a common amino acid.]] | [[Image:Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg|right|thumb|350px|{{#ifexist:Template:Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg/credit|{{Aspartic acid stick figure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}'''Aspartic acid''', a common amino acid.]] | ||
'''Aspartic acid''', abbreviated as '''Asp''' or '''D''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is a charged, polar, [[hydrophilic]] amino acid, and it is thus often found on the outer surface of proteins. At physiological pH, the acidic side chain is deprotonated. It is one of the two acidic amino acids, the other being [[glutamic acid]]. It is similar to the amino acid [[asparagine]], in which the acid group is replaced by an amide group. [[Canavan disease]] is associated with the built up of the N-acetylated form of aspartic acid. | '''Aspartic acid''', abbreviated as '''Asp''' or '''D''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is a charged, polar, [[hydrophilic]] amino acid, and it is thus often found on the outer surface of proteins. At physiological pH, the acidic side chain is deprotonated. It is one of the two acidic amino acids, the other being [[glutamic acid]]. It is similar to the amino acid [[asparagine]], in which the acid group is replaced by an amide group. [[Canavan's disease]], an inherited neurological disease primarily effecting children of eastern and central European Jewish descent (Ashkenazi), is associated with the built up of the N-acetylated form of aspartic acid. | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 17 January 2008
Aspartic acid, abbreviated as Asp or D, is one of the twenty common amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. It is a charged, polar, hydrophilic amino acid, and it is thus often found on the outer surface of proteins. At physiological pH, the acidic side chain is deprotonated. It is one of the two acidic amino acids, the other being glutamic acid. It is similar to the amino acid asparagine, in which the acid group is replaced by an amide group. Canavan's disease, an inherited neurological disease primarily effecting children of eastern and central European Jewish descent (Ashkenazi), is associated with the built up of the N-acetylated form of aspartic acid.