Archive:Fair Use Policy, Media
THE FOLLOWING IS ONLY A DRAFT FOR A PROPOSED POLICY AND SHOULD NOT BE RELIED UPON IN ANY WAY. IT HAS BEEN POSTED TO RECEIVE COMMUNITY INPUT. PLEASE OFFER DEBATE ON THE FORUM THREAD. OFFER SUGGESTED CHANGES ON THE TALK PAGE.
DISCLAIMER:
The following is not legal advise but Citizendium policy guidance. Qualifying to make a fair use claim on Citizendium does not imply that such a claim is, in fact, fair use. The onus of any such claim rests upon the uploader of such content, who is advised to make their own, independent evaluations of their fair use claims in consultation with appropriate legal counsel. For content uploaded by Citizendium contributors as fair use, the onus of their claims rest solely upon re-users of Citizendium content. Potential and actual re-users of Citizendium content are advised to make their own, independent evaluations of all Citizendium content prior re-use, in consultation with appropriate legal counsel.
Fair use is a necessarily difficult yet navigable area of Citizendium policy. For better or for worse, it is often labor-intensive as well. Legal scholars have described the "fair use" doctrine as "a murky concept in which it is often difficult to separate the lawful from the unlawful."[1] Confounding this, there is only one sure way to tell whether the particular use you claim as "fair" really is: by having the matter resolved in federal court.[2]
Citizendium's policy on fair use is designed to steer contributors toward the "clear" side of these murky waters, to try to avoid the precarious situation of fair use challenges toward both its contributors and itself, to not prohibit fair use media altogether, and to make determinations over fair use as straightforward as possible. Citizendium's "fair use" policy largely follows that of reputable scholarly journals, while balancing and incorporating into the mix Citizendium's ideals of providing so-called "free" (libre) content to re-users.
Usage of "fair use" media on Citizendium is governed by the five tests that follow. When passed, they lead to the requirement of writing a strong and detailed fair use rationale on the image's upload page.
TEST ONE: Can a "free" substitute be found or created?
The most straightforward way to avoid troubles over fair use is to avoid invoking the doctrine at all. To this end you should apply TEST ONE before even considering whether to make a fair use claim.
TEST ONE: Have you given a reasonably sustained effort to obtain a substantially equivalent "free" substitute, or could such be created within a reasonable time frame?
- If YES, then go on to TEST TWO.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
NOTE: A new good-faith attempt to locate "free" replacements of non-"free" images in articles should occur during the period between all approval and re-approval nominations and actual approval.
TEST TWO: Has an editor nominated the article for approval?
As a crucially important bolster for fair use claims, all articles in which fair use images appear must strictly adhere to Citizendium's Neutrality Policy. Fair use images should not appear in articles until any neutrality issues are settled. It is assumed that articles nominated for approval by an editor will be free from any serious neutrality issues. Of course, editors are disinclined to give their approval to articles with evident neutrality issues, and are specifically instructed to withhold from doing so.
TEST TWO: Has the article been nominated for approval?
- If YES, then go on to TEST THREE.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
NOTE: To facilitate rapid placement of all "fair use" images after approval nomination, it is suggested that the image sources be collected in a section on an article's talk page.
TEST THREE: Does your fair use claim clearly fit into one of the categories below?
Category One: Coats of Arms, flag emblems, seals, etc., of administrative entities, political authorities and institutions
Given the following six conditions:
- The image must be obtained from the official source.
- The image may only appear in an article specifically about such entities.
- A disclaimer must be placed at the top of the top of the article stating, This is not an official page of [http://www.entitydomain.com|Entity name]. For such entities without a web presence, simply place the name.
- The image must be of the highest available quality yet only in size and resolution sufficient for adequate displaying of information.
- The image must appear in a box with text stating it is "The official [flag, seal, etc.] of [entity]."
Does your fair use claim clearly fall into Category One?
- If YES, your upload DOES qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium. Go now to Making a strong fair use claim.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
Category Two: Currency, stamps, vehicle license tags

Image courtesy of Bank of Latvia.
Given the following two conditions:
- The image must be obtained from its official issuing source.
- It must appear appear in an article about that which the image depicts.
Does your fair use claim clearly fall into Category Two?
- If YES, your upload DOES qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium. Go now to Making a strong fair use claim.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
Category Three: Company logos, trademarks, and copyrighted packaging

Image courtesy of The Coca-Cola Company.
- NOTE: An example of copyrighted packaging would be a "slavish copy" of a package of Lipton Tea.
Given the following six conditions:
- The image must be obtained from its source.
- The image may only appear in an article:
- a. Specifically about the company or product whose logo, trademark, or copyrighted packaging is being used.
- b. About or discussing logos and/or trademarks and/or or copyrighted packaging in some way, in which case the examples chosen must be discussed specifically and must be of an iconic nature.
- A disclaimer must be placed at the top of the top of the article stating, This is not an official page of [http://www.companydomain.com|Company name (and product, if applicable)]. For companies and products without a web presence, simply place the company and product name.
- The image must be good quality, i.e., not blurry and preferably in PNG format, yet only in size and resolution sufficient for adequate displaying of information
- The image must appear in a box with text stating, "The official [logo, trademark, packaging] of [company or product]," e.g., "The official Coca-Cola trademark of the Coca-Cola Company."
Does your fair use claim clearly fall into Category Three?
- If YES, your upload DOES qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium. Go now to Making a strong fair use claim.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
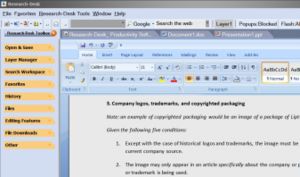
Image courtesy of Winferno Software.
Category Four: Software screen captures
Given the following four conditions:
- The software screen capture must illustrate a specific point within the article.
- Partial screen captures of software must be used whenever possible.
- The software screen capture must be as small as possible to convey the information. See and click on the example to the right.
- If full screen, the image must be no more than about 10% of the original pixel size as might be displayed on a typical 15 inch (38 cm) computer screen.
- The image should be self-made, or in no way subject to another's copyright.
Does your fair use claim clearly fall into Category Four?
- If YES, your upload DOES qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium. Go now to Making a strong fair use claim.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.

Image courtesy of Allworth Press.
Category Five: Book, periodical, CD and other disc covers, and promotional posters
Given the following two conditions:
- 1. The image must be in an article about one of the following:
- a. The book, periodical or periodical edition, disc, or poster event itself.
- b. The author, artist, or publisher, in which case a section of the article must be about the book, periodical or periodical edition, album, disc, or poster event itself.
- c. The person, group, or historical event that appears on the cover of the periodical, in which the periodical's coverage of the person, group, or historical event must be a specific subject of discussion.
- d. A subject of which the periodical, disc, or poster event is a subject, in which case the image thereof must be specifically discussed in the article.
- NOTE: Pictorial depictions of a person or group on any such cover may not used as the lead image for an article about the person or group.
- 2. The image as uploaded is very closely the same size and resolution as the example book cover shown to the right.
Does your fair use claim clearly fall into Category Five?
- If YES, your upload DOES qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium. Go now to Making a strong fair use claim.
- If NO, then skip to TEST FOUR.
TEST FOUR: Can you prove permissions diligence/frustration?
It is believed that most fair use claims outside of the above five categories of TEST THREE can be avoided by diligent seeking of permission. However, there are two instances where this may not be the case.
The missing copyright holder
In cases where you have diligently but fruitlessly attempted to locate the copyright holder, and you can prove such attempts (by documenting them on a /Permission subpage of the image's talk page), authorities are unanimous that your fair use claim is greatly bolstered and that you'd typically avoid paying anything beyond a normal usage fee should the copyright-holder later show up and take you to court. To this end you should apply the Permissions Diligence Test, TEST FOUR, before even considering whether to make a fair use claim beyond those provided for in TEST THREE.
TEST FOUR "A": Have you diligently but unsuccessfully attempted to contact the copyright owner to ask permission, and are you prepared to document those attempts on a subpage of the image's talk page?
- If NO, your upload DOES NOT qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium.
- If YES, then go on to TEST FIVE.
NOTE: For an example of a thus far unsuccessful permission attempt see Talk:Tux/lin64; for an example of a thus far probably successful but as yet inconclusive attempt see Talk:Tux/ccpenguin.jpg; for examples of successful attempts see Image talk:Wessel 1954 fig1.png/Permission and Image talk:Gilad Atzmon - for Citizendium.jpg/Permission.
- Note: The volunteers of Citizendium's Media Help Center are available to serve you in obtaining images, and permissions therefor as needed.
Fee barriers
It is anticipated that most copyright holders will grant permission to Citizendium contributors without fee. This will certainly not always be the case, however. In some cases, fees may be simply unrealistic for a free encyclopedia project, or you may not wish to pay a fee regardless. If so, you should request assistance from Citizendium's Media Help Center before even considering whether to make a fair use claim beyond those provided for in TEST THREE. The Media Help Center may be able to negotiate with the copyright holder with more leverage.
TEST FOUR "B": In the case of fees you are unwilling to pay, has Citizendium's Media Help Center unfruitfully concluded your request for assistance?
- If NO, your upload DOES NOT qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium.
- If YES, then go on to TEST FIVE.
TEST FIVE: Is it really fair use?
The law of fair use, having been developed by courts since the 1800s, has since been codified in the United States Copyright Act, 17 USC § 107:
§ 107. Limitations on exclusive rights: Fair use
- Notwithstanding the provisions of sections 106 and 106A, the fair use of a copyrighted work, including such use by reproduction in copies or phonorecords or by any other means specified by that section, for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching (including multiple copies for classroom use), scholarship, or research, is not an infringement of copyright. In determining whether the use made of a work in any particular case is a fair use the factors to be considered shall include—
- the purpose and character of the use, including whether such use is of a commercial nature or is for nonprofit educational purposes;
- the nature of the copyrighted work;
- the amount and substantiality of the portion used in relation to the copyrighted work as a whole; and
- the effect of the use upon the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work.
- The fact that a work is unpublished shall not itself bar a finding of fair use if such finding is made upon consideration of all the above factors.
Thus, TEST FIVE is:
TEST FIVE: If after carefully reviewing the above fair use criteria, are you convinced your claim of fair use is fair use indeed, and are you prepared to bear complete responsibility with the copyright holder if you are wrong?
- If NO, then your upload DOES NOT qualify for a fair use claim on Citizendium.
- If YES, then proceed to Making a strong fair use claim.
Making a strong fair use claim
If you have been instructed that you may make a fair use claim in a Citizendium article, you should carefully and in detail document your reasons for believing in your claim, answering the following questions on the media upload the page:
Justifying "fair use" means making your case concerning:
- the purpose and character of the use, including whether such use is of a commercial nature or is for nonprofit educational purposes;
- the nature of the copyrighted work;
- the amount and substantiality of the portion used in relation to the copyrighted work as a whole; and
- the effect of the use upon the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work.
Additionally:
- The media upload page should include:
- A neutral description of the image.
- A link to the official source page of the image (but don't link directly to the image on the server).
- A link to the copyright holder.
- The article in which the fair use image appears should include:
- Image courtesy of [Name of copyright holder] within the image box.
See the examples above for models.
References and footnotes
- ↑ "Disagreements Over Fair Use: When Are You Likely to Get Sued?" http://fairuse.stanford.edu/Copyright_and_Fair_Use_Overview/chapter9/9-d.html
- ↑ Measuring Fair Use: The Four Factors http://fairuse.stanford.edu/Copyright_and_Fair_Use_Overview/chapter9/9-b.html
Additional reading
- Digital History: A Guide to gathering, Preserving, and Presenting the Past on the Web — by the Center for History and New Media, George Mason University