Phishing
Phishing is the computer industry term used to describe a type of fraud in which the victim is encouraged to divulge personal confidential information, such as an account username and password for an online banking or financial service. The term, with its unusual spelling, derives from the associated but older term phreaking, which refers to hacking into telephone systems.
A typical phishing attempt uses social engineering techniques to prey on the fears of uninformed users of online financial systems. By tricking such users into divulging their account credentials, the fraudsters can then access the compromised accounts and transfer the funds therein to a holding account, which will then be quickly emptied.
Method
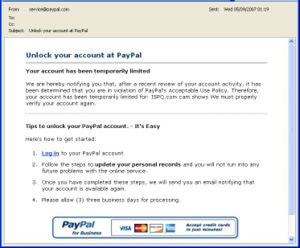
The fraudsters will first set up a page or pages on a website, designed to mimic that of their target financial institution. Quite often, the pages will be uploaded to an innocent website that has been hacked; the legitimate owner of the website will be unaware that it is being used in this fashion. Then, using a bot network or other similar means, the perpetrators will send a carefully constructed email to a massive number of recipients. The email will use copied logos, embedded in the mail, to give the appearance that it is coming from the financial institution in question. It will generally employ email spoofing methods to disguise the sender's address and to make it appear as if it is coming from the financial institution in question.
While many of these mails will be caught by spam filters and other protections, some will make it through to the mailboxes of people who have accounts with the target financial institution. A person clicking on one of the links contained in the email will be brought not to the financial institution's website, but to the fake one that has previously been set up. If the mail recipient does not notice that they are at a fake site and enters their credentials, the fake site will record these details. The fraudsters can then access the account themselves and empty it of funds.
The image to the right shows one such typical email. The example represents a relatively poor attempt at a phishing mail. Notice the lack of an entry in the "To:" field of the email; lack of a personalised greeting; and the very unclear (and ungrammatical) reason stating why the person's details are required: "<website> cam shows We must properly verify your account again." The faked logo is used only once. Phishing mails can often be far more sophisticated.

Clicking on a link in the above email brings the user to the website pictured left. Again, this is not a very sophisticated example, but much more believable sites are used. In this screenshot, we can see that although the website purports to be Paypal, the browser address bar is that of a completely different site. Similarly, hovering the cursor over a hyperlink shows that by clicking on a link, the user will be brought to a page not hosted by Paypal.
Faked sites have been made to look more convincing by several methods. Two common examples include using scripts hosted on the website, which serve to disguise the website's address as displayed in the address bar and to disguise the true destination of hyperlinks as displayed in the status bar; and to construct a website address using non-standard characters, which nonetheless appear at a casual glance to be that of the expected website.
Cost
As far back as 2004, Gartner Research estimated that the cost of phishing frauds to banks and credit card companies was US$1.2 billion, in the United States alone.[1]
Effectiveness
Unfortunately for financial institutions and victims of phishing attempts, this method of fraud has proven to be highly successful. The main cause is a lack of knowledge and education about online safety on the part of end users. While the computer is ubiquitous in most developed countries and people have taken to the convenience of online services, few take the trouble to keep abreast of the latest security threats.
While computer users may therefore be vaguely aware of threats to the security of their online accounts, they may not be aware of the specifics involved - despite efforts by financial institutions to educate them. Therefore when they receive an email purporting to come from their bank, possibly warning (as many phishing mails do) that their account may have been compromised and that they need to verify their credentials, they follow the instructions without the necessary knowledge to detect a fraudulent email or website.
Financial institutions themselves may have partly contributed to this problem - many use website addresses for their online banking functions that are substantially different from the bank's normal internet domain. Similarly, many regularly email their customers from addresses different to the normal domain.
Protection
There are two main methods of preventing successful phishing attacks. The first is user education. This involves educating end-users of online financial websites about the reality and methods of identity theft, including phishing, and advising them of the methods to avoid falling for such frauds. As outlined above, this has proven to be a difficult task.
The second method is to use software that will intervene to directly warn the user when a possible phishing attempt is detected, or otherwise make the fraudsters' emails and websites more obvious as fakes. Both Microsoft's Outlook email program and Google's web-based Gmail, to give but two examples, attempt to deter users from accessing phishing emails. Outlook does this by requiring user intervention before displaying graphics embedded in an email - and presumably the end user will wonder why they need to authorise a download from their financial institution, which would likely already have been authorised. Gmail places a warning directly onto each email it perceives as a phishing attempt.
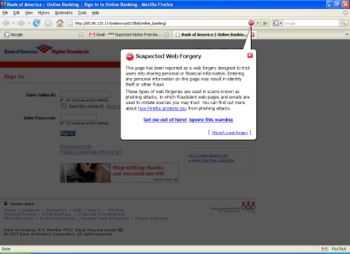
Similarly, some web browsers will alert users to potential phishing websites. Pictured right, is the very obvious popup deployed by the Firefox web browser (version 2.0.0.6) to alert the user that a potentially fraudulent website has been visited. The web page is greyed out, and the user is warned, given the option of getting more information, or continuing - but can't interact with the web page until they have chosen one or the other.
Another line of defense using software is the newest generation of security suite, which in addition to the usual anti-virus and firewall software, may now contain anti-malware features including detection of phishing attempts.
References
- ↑ Internetnews.com: Cost to business of phishing: Available: http://www.internetnews.com/ec-news/article.php/3350891 Retrieved: 5th September 2007.