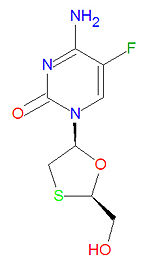
Emtricitabine
|
| |||||||
| emtricitabine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | HIV | ||||||
| Properties: | Reverse transcriptase inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Emtricitabine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) antiviral drug used to treat HIV/AIDS. Emtricitabine is a synthetic analogue of cytidine and is similar in structure to the drugs zalcitabine and lamivudine. Once the drug in converted to the triphosphate form, it works by inhibiting reverse transcriptase, the enzyme that copies HIV RNA into new viral DNA, by competing with the natural DNA base deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP). Once it is incorporated into a growing viral DNA strand, it acts as a chain terminator because it lacks a 3'-hydroxy group needed for form a phosphodiester linkage to the next incoming DNA base. It is usually used in combination with other anti-HIV drugs.
Chemistry
It IUPAC chemical name is 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-[(2R,5S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]pyrimidin-2-one and its chemical formula is C8H10FN3O3S. It is sold as a single drug under the trade names Coviracil®, Emtriva® and Racivir® and in combination with other antiviral drugs as Truvada® (with tenovir) and Sustiva® (with tenovir and efaverenz).
References
External links
- Emtricitabine - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank