Docosahexaenoic acid
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
| |||||||
| docosahexaenoic acid | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | natural nutrient | ||||||
| Properties: | omega-3 fatty acid | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
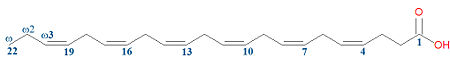
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), more correctly called docosa-4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid, is a naturally occuring omega-3 fatty acid. It is a fatty acid that contains a linear chain of twenty-two carbon atoms, with double bonds occuring at six positions, all with the cis configuration. It is called an omega-3 fatty acid because from the aliphatic end of the molecule, always referred to as the omega carbon, the first double bond occurs at carbon 20, the omega-3 carbon. Like other omega-3 fatty acids, it can be found in fish.
Synonyms
- 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid
- cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid
- (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid (IUPAC)
- all Z-docosahexaenoic acid
- all cis-docosahexaenoic acid
- Cervonic acid
- Cervonate