Noctiluca scintillans
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
| Noctiluca scintillans | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||
|
Description and Significance
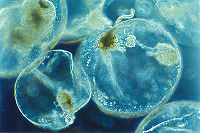
Noctiluca scintillans, also known as sea sparkles, are single-celled dinoflagellates that exhibit bioluminescence. They are free-living marine plankton, which range between 200-2000 micrometers in diameter. They are found mostly in estuaries and other coastal regions and can be found in both warm and cold waters. N. Scintillans are heterotrophic and non-photosynthetic, meaning they receive their carbon from organic compounds and receive their energy through the ingestion of organic substances. They don’t have any chloroplasts so, their cytoplasm is relatively clear. Noctiluca scintillans are non-motile, even though they possess a flagellum, and only move vertically by changing their buoyancy using gas vacuoles. N. Scintillans can reproduce asexually, by binary fission, and sexually, using isogametes through a diplontic lifecycle.
The bioluminescent property of N. scintillans is a tourist attraction for many countries throughout the world. People would take boat rides and watch these dinoflagellates emit flashes of blue light when disturbed, giving them the name sea sparkle.
Genome and Structure
The entire genome for Noctiluca scintillans has not been sequenced. However many studies have been done on the luciferase gene within the scintillons of this species. They have found that Noctiluca scintillans is genetically distinct from the other six bioluminescent dinoflagellates that have been studied, because the N-terminal is missing a ~100aa sequence. Still the N-terminal is closely related to the other bioluminescent dinoflagellates. The C-terminal of this gene, however, is closely related to a separate gene in a photosynthetic dinoflagellate. It is as if these two genes in the photosynthetic species were fused in N. scintillans. Studies of the 18S ribosomal DNA of N. scintillans, also suggested that they were one of the first species to branch off because their genomic sequence is most closely related to the ancestral gene.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
Noctiluca scintillans has a round, balloon-like, body shape and is unarmored, meaning it does not have a protective shell. Since they do not photosynthesize, they don’t have chloroplasts and thus are fairly clear. The red and green color usually associated with this species, in the red and green tides, are due to the pigments of the photosynthetic symbionts within the vacuoles of N. scintillans and not the species itself. N. scintillans have a ventral groove that run through their bodies which contains the flagellum, a tooth and a tentacle. They also have a mouth-like structure called the cytostome which they use to capture and consume prey.
Noctiluca scintillans is a phagotrophic species with many food vacuoles found throughout their cytoplasm. They engulf smaller marine species such as diatoms, protozoans, fish eggs, and certain bacteria and then digest them in these food vacuoles. N. scintillans also contain gas vacuoles, which are filled with ammonia gas, that allow them to control their buoyancy.
Small cytoplasmic bodies within the cells, called scintillons, are what give N. scintillans their bioluminescent property. Luciferase and luciferin are both found in those structures and it is the interaction of both these molecules that emits light.
Ecology and Pathology
Noctiluca scintillans are found mostly in coastal areas, in both temperate and tropical waters. Their population density has been found to be dependent on food availability, which is why they tend to stay in shallow, coastal areas, where phytoplankton thrive. They are also a major factor on the population density of zooplankton.
Noctiluca scintillans are sometimes known to have a large population boom known as red or green tides (depending on what color endosymbionts are present in their vacuoles.) These tides cause the death of many marine animals. N. scintillans does not, however, release exotoxins like many other dinoflagellates do. Instead, it is believed that they kill these animals by suffocation due to the release of ammonia and carbon dioxide, causing anoxic water conditions.
Application to Biotechnology
Current Research
References
Noctiluca : Sparkle of the sea. 1995. Microscopy-UK. April 2009. http://www.microscopy- uk.org.uk/mag/indexmag.html?http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/art98/nocti.html
Identifying Harmful Marine Dinoflagellates. Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History Botany Department. April 2009. http://botany.si.edu/references/dinoflag/Taxa/Nscintillans.htm
Nakamura, Yasuro. "Biomass, feeding and production of Noctiluca scintillans in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan." Journal of Plankton Research. 20.11 (1998): 2213-2222
Noyan Yilmaz, Erdoğan Okus¸ and Ahsen Yüksek. "Evidences for influence of a heterotrophic dinoflagellate (Noctiluca scintillans) on zooplankton community structure in a highly stratified basin." Estuarine, Coastal, and Shelf Science. 64.2-3 (2005): 475-485
"Ride Tide of Noctiluca Scintillans and it's Impact on the Coastal Water Quality of the Near-Shore Waters, Off the Rushikulya River, Bay of Bengal." Current Science. 93.5 (2007): 616-617
Al-Azri, Adnan. "Seasonality of the Bloom-Forming Hetertrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca Scintillans in the Gulf of Oman in Relation to Environmental Conditions." International Journal of Oceans and Oceanography. 2.1 (2007): 51-60
Liu, Liyun. "Two Different Domains of the Luciferase Gene in the Heterotrophic Dinoflagellate Noctiluca Scintillans Occur as Two Separate Genes in Photosynthetic Species." PNAS. 104.3 (2007): 696-701
Hoppenrath, Mona and Juan F. Saldarriaga. 2008. Dinoflagellates. Version 16 September 2008 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Dinoflagellates/2445/2008.09.16 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/
Asare, Amma. Bioluminescence. Milton Academics Marine Biology Department. http://www.milton.edu/academics/pages/marinebio/biolum.html