Comparative biology
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(CC) Image: Mabuchi et al., 2007
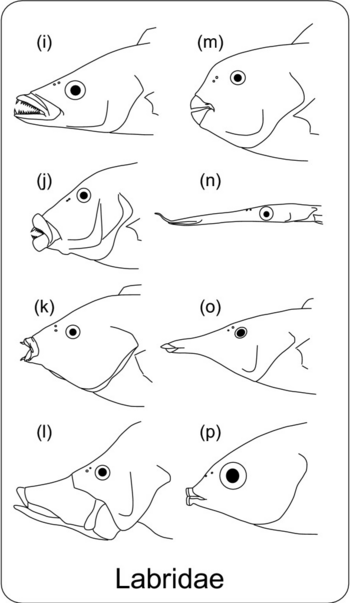
Diversity of the skull in the labrid fish. (i) Cheilinus celebicus, feeds on small fishes and invertebrates, (j) Hemigymnus melapterus, feeds on invertebrates in sand, (k) Anampses geographicus, feeds on small hard-shelled invertebrates, (l) Epibulus insidiator, engulfs crustaceans and small fishes, (m) Chlorurus microrhinos, feeds on the epilithic algal matrix of coral reefs, (n) Siphonognathus argyrophanes, feeds on small invertebrates picked from weeds or the substratum, (o) Gomphosus varius, feeds on small benthic crustaceans, (p) Labrichthys unilineatus, a coral-polyp eater.
Diversity of the skull in the labrid fish. (i) Cheilinus celebicus, feeds on small fishes and invertebrates, (j) Hemigymnus melapterus, feeds on invertebrates in sand, (k) Anampses geographicus, feeds on small hard-shelled invertebrates, (l) Epibulus insidiator, engulfs crustaceans and small fishes, (m) Chlorurus microrhinos, feeds on the epilithic algal matrix of coral reefs, (n) Siphonognathus argyrophanes, feeds on small invertebrates picked from weeds or the substratum, (o) Gomphosus varius, feeds on small benthic crustaceans, (p) Labrichthys unilineatus, a coral-polyp eater.

(CC) Image: CZ:Ref:Brown 2007 Xenopus tropicalis egg extracts provide insight into scaling of the mitotic spindle
Mitotic spindles (bottom) are about 30% longer in Xenopus laevis (green) than in its smaller, faster-breeding relative, X. tropicalis (red).
Mitotic spindles (bottom) are about 30% longer in Xenopus laevis (green) than in its smaller, faster-breeding relative, X. tropicalis (red).