Gene duplication
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Gene duplication is the insertion of the same gene into different parts of the genome of an organism. This typically occurs as the result of copying errors during cell division, though it can also occur if an existing gene is incorporated again by means of horizontal gene transfer.
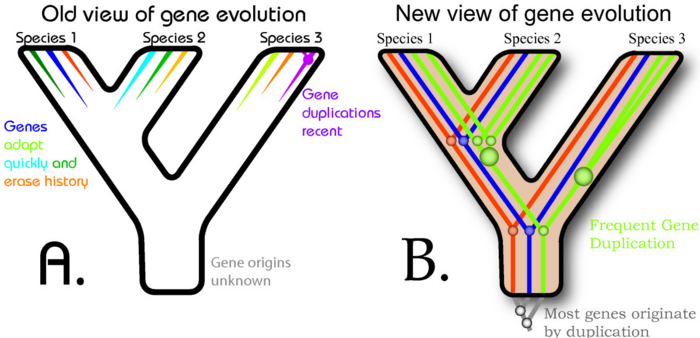
(CC) Image: Rose & Oakley, 2007
Two views on the role of gene duplication in evolution. (A) Many 20th century biologists viewed genes as traits of species, exquisitely tuned to current utility. This resulted in the assumption that each species should, for the most part, possess different genes. Gene duplication was recognized, but was implicitly assumed to have occurred recently. (B) Many biologists now assume that most genes have their origins in gene duplication events, which happen throughout evolutionary history. As a result, many genes form families that have persisted for hundreds of millions of years.
Two views on the role of gene duplication in evolution. (A) Many 20th century biologists viewed genes as traits of species, exquisitely tuned to current utility. This resulted in the assumption that each species should, for the most part, possess different genes. Gene duplication was recognized, but was implicitly assumed to have occurred recently. (B) Many biologists now assume that most genes have their origins in gene duplication events, which happen throughout evolutionary history. As a result, many genes form families that have persisted for hundreds of millions of years.