Neuron
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
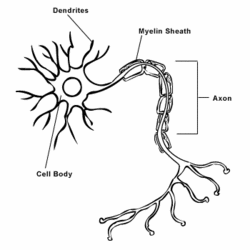
In biology, a neuron is a cell that specializes in information transfer, and the fundamental unit of the nervous system.[1] Neurons can initiate and transmit the electrical signals necessary for the proper function of most biological organisms. Typically, neurons can be divided into three regions which allow them to receive and transmit signals. Neurons have a body or soma which contain the cell nucleus and other organelles which are required for normal cell functioning. Neurons also have dendrites which allow them to receive information, and axons which allow them to transmit signals to other neurons in the organism.[2]
References
- ↑ Zigmond M, et. al., eds. (1999) Fundamental Neuroscience ISBN 0127808701
- ↑ Purves D, et. al., eds. (1997) Neuroscience ISBN 0878937471