Chlorella minutissima
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
| Chlorella minutissima [1] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[[image: |200px|]] |200px|]] | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Chlorella minutissima |
Description and significance
Chlorella Minutissima is a unicellular marine alga that has chlorophyll a and b, and synthesizes starch, like plants. The microalgae is spherical in shape and lack a flagella. Chlorella, from Greek word chloros, green and the Latin suffix ella means "small" .Some sources classify algae as plants, such as the Australian Antarctic Data Centre. [2] However, algae are more often categorized into Kingdom Protista, which belongs to domain Eukarya. Therefore algae have membrane enclosed nucleus, yet the internal structures of algae are simpler than those of plants. Chlorella minutissima is rich in amino acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5co3), which makes Chlorella Minutissima potentially useful in health foods and pharmaceuticals.[3] In the past Chorella Minutissima has been considered to be used as a protein source to the world population to solve the problem of hunger due to two World Wars and the increasing population. Scientists later found that to produce Chlorella Minutissima massively under ideal conditions, the condition would cost a very high cost to maintain. The microalgae is an important component in finfish and shellfish aquaculture[4], therefore research has been done in maximizing the growth and storage of Chlorella Minutissima.
Genome structure
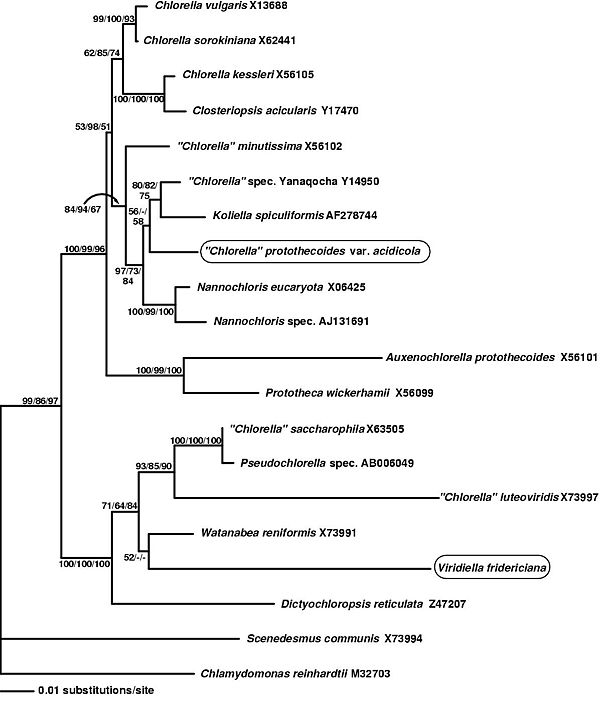
Nuclear-encoded small subunit ribosomal RNA gene (18SrDNA) sequences of Chlorella Minutissima and closely related speices were determined[5] There is little published information on the genome of Chlorella minutissima. The microbe is haploid and lacks a sexual cycle, therefore it is not useful in the study of genetics.
Cell structure and metabolism
Chlorella minutissima is unicellular without flagella. The growth of Chlorella minutissima does not require the presence of secondary carotenoids, thiamine and vitamin B12. The lower limit of pH toleration of Chlorella minutissima is 5.5 and the upper temperature limit of growth is 32°C. The maximam toleration to NaCl is 1%[5] Research on Chlorella minutissima has been performed to test the composition of fatty acids under various conditions. The growth of Chlorella minutissima in low light intensity is about 1/5 of that in high light intensity. Light intensity has little effect on total content of fatty acid, but it does affect the compostion of fatty acids[6]
Ecology
Application to Biotechnology
Health foods and pharmaceuticals Chlorella minutissima has high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5ω3), which is important for mammals as an agent to prevent blood platelet aggregation. 20:5ω3 is also one of the precursors for prostaglandin. Since the synthesis of ω3 PUFA in marine fishes is very low and marine fishes acquire ω3 from diet, it is tempting to speculate that people may benefit from ingesting marine microalgae and receive polyunsaturated fatty acids<ref name=Akira>.
Current Research
References
- ↑ =http://www.uniprot.org/taxonomy/3081
- ↑ =http://data.aad.gov.au/aadc/biodiversity/taxon_profile.cfm?taxon_id=116567
- ↑ =Seto,A., Wang,H.L. and Hesseltine,C.W. Culture Conditions Affect Eicosapentaenoic Acid Content of Chlorella minutissima. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, Volume 61, Number 5. May, 1984, p.892-894
- ↑ = Tzovenisa, I., Triantaphyllidisb, G., Naihongc, X., Chatzinkolaoua, E., Papadopouloua, K., Xouria, G., Tafasa, T. Cryopreservation of marine microalgae and potential toxicity of cryoprotectants to the primary steps of the aquacultural food chain. Aquaculture, 230, 2004, p.457–473
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Volker AR Huss, Claudia Ciniglia, Paola Cennamo, Salvatore Cozzolino,Gabriele Pinto and Antonino Pollio. Phylogenetic relationships and taxonomic position of Chlorella-like isolates from low pH environments (pH < 3.0). BMC Evolutionary Biology, 26 August 2002. 2:13
- ↑ AKIRA SETO 1, H.L. WANG and C.W. HESSELTINE. Culture Conditions Affect Eicosapentaenoic Acid Content of Chlorella minutissima. Northern Regional Research Center, Agricultural Research Service, USDA, Peoria, Illinois 61604