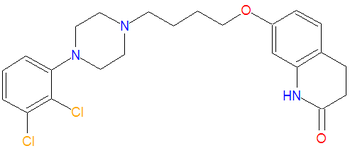
Aripiprazole
|
| |||||||
| Aripiprazole | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antipsychotic agent | ||||||
| Properties: | medication | ||||||
| Hazards: | see side effects & drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
In medicine, aripiprazole (pronunciation: ay ri pip' ray zole) is an atypical or second generation antipsychotic agent that "has both presynaptic dopamine autoreceptor agonistic activity and postsynaptic D2 receptor antagonistic activity; structure given in first source; use associated with hyperglycemia."[1]
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of aripiprazole for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar I disorder, major depressive disorder, irritability associated with autistic disorder agitation associated with schizophrenia or mania from bipolar disorder. It is also approved as an adjunct to antidepressants.[2] The trade name is Abilify™. Although not approved for the treatment of dementia, aripiprazole has been studied in this setting.
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Aripiprazole (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Marianna Mazza, Maria Rosaria Squillacioti1, Riccardo Daniele Pecora, Luigi Janiri1 & Pietro Bria (December 2008), "Beneficial acute antidepressant effects of aripiprazole as an adjunctive treatment or monotherapy in bipolar patients unresponsive to mood stabilizers: results from a 16-week open-label trial", Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 9 (18): 3145-3149, DOI:10.1517/14656560802504490