Warfarin
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
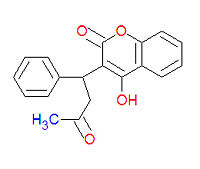
Warfarin (IUPAC name 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-chromen-2-one), also widely called coumadin, is a an anticoagulant medication used prophylactically to suppress the formation of thrombosis and embolism. It was originally designed to be a rat poison. It works as an anticogulant by suppressing the enzyme epoxide reductase in the liver, thereby suppresing the formation of the reduced form of vitamine K epoxide, which is needed for the synthesis of many coagulation factors. As a drug, it is often sold as the sodium salt of warfarin.
Brand names
- Athrombin
- Athrombin-K
- Athrombine-K
- Brumolin
- Co-Rax
- Coumadin
- Coumafen
- Coumafene
- Coumaphen
- Coumaphene
- Coumarins
- Coumefene
- D-Con
- Dethmor
- Dethnel
- Dicusat E
- Frass-Ratron
- Jantoven
- Kumader
- Kumadu
- Kumatox
- Kypfarin
- Latka 42
- Mar-Frin
- Marevan
- Maveran
- Panwarfin
- Place-Pax
- Prothromadin
- RAX
- Rosex
- Sofarin
- Solfarin
- Sorexa Plus
- Temus W
- Tintorane
- Tox-Hid
- Vampirinip II
- Vampirinip III
- Waran
- Warf 42
- Warfarat
- Warfarin Plus
- Warfarin Q
- Warfarine
- Warficide
- Warfilone
- Zoocoumarin
References
External links
- Warfarin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).