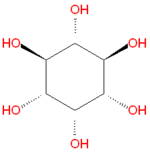
Inositol
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Inositol refers to a collection hexose carbohydrates based on a central cyclohexane structure with six hydroxyl (OH) groups. Although myo-inositol, previously called meso-inositol, is the most common version found in nature, a number of other stereoisomeric forms are produced naturally. Inositol acts as a fatty acid transport by coupling its hydroxyl oxygen atoms with the carboxyl groups of fatty acids. The stereochemistry of myo-inositol is denoted by the IUPAC name cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-cyclohexanehexol.