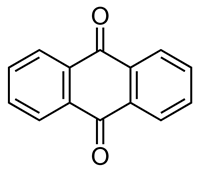
Anthraquinone
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

Anthraquinone is the class-defining compound for a number of naturally-occurring plant pigments. Anthraquinone itself has been associated with causing liver, bladder and kidney cancers, and other non-neoplastic disorders.[1]. It also, however, has been a starting point for developing antineoplastic agents, especially the anthracycline agents, of which doxorubricin (Adriamycin) is best known. [2]
The plant Rheum palmatum, called Indian rhubarb in North America and also used in traditional Chinese medicine is rich in anthraquinones.
Anthraquinone derivatives called sennosides are used as cathartics; they are the active principle in senna extract.
References
- ↑ TR-494 Anthraquinone, National Toxicology Program, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- ↑ Lown JW (1993 Nov), "(Abstract) Anthracycline and anthraquinone anticancer agents: current status and recent developments.", Pharmacol Ther 60 (2): 185-214